焦點新聞
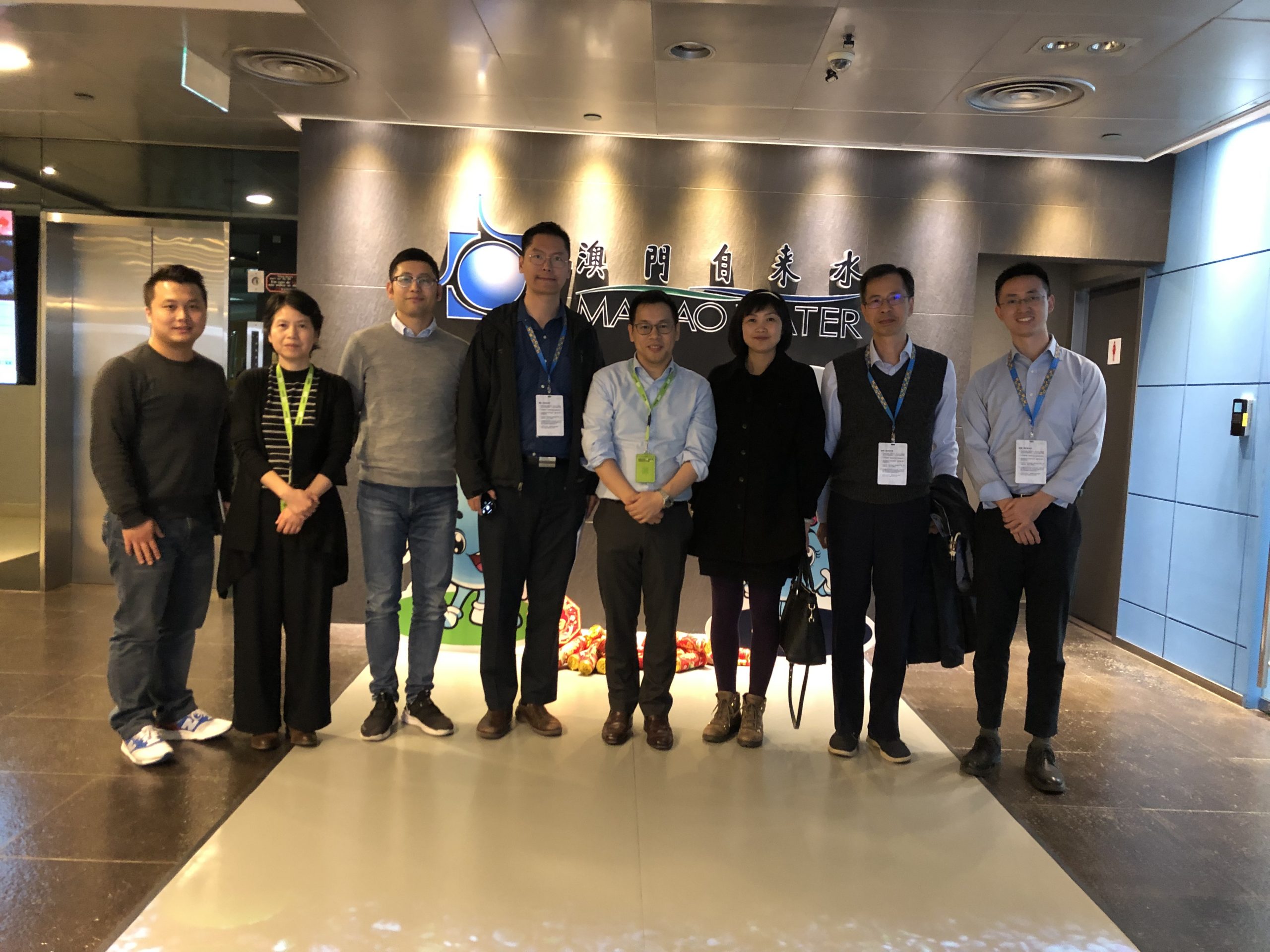
蘇伊士與澳門大學攜手創新研究 致力於保護海洋環境
積極拓展區域海洋環境領域的研究是澳門大學的科研戰略佈局中重要一環,藉著世界海洋日,澳大與蘇伊士及旗下澳門自來水股份有限公司宣佈簽署合作框架協議,三方通過整合各方在科研和海洋環境保護上的資源與優勢,建立高水準的科研合作平台,開展近海環境生態與水處理技術等相關領域的創新性研究,攜手保護海洋環境及豐富海洋生物多樣性。
[…]
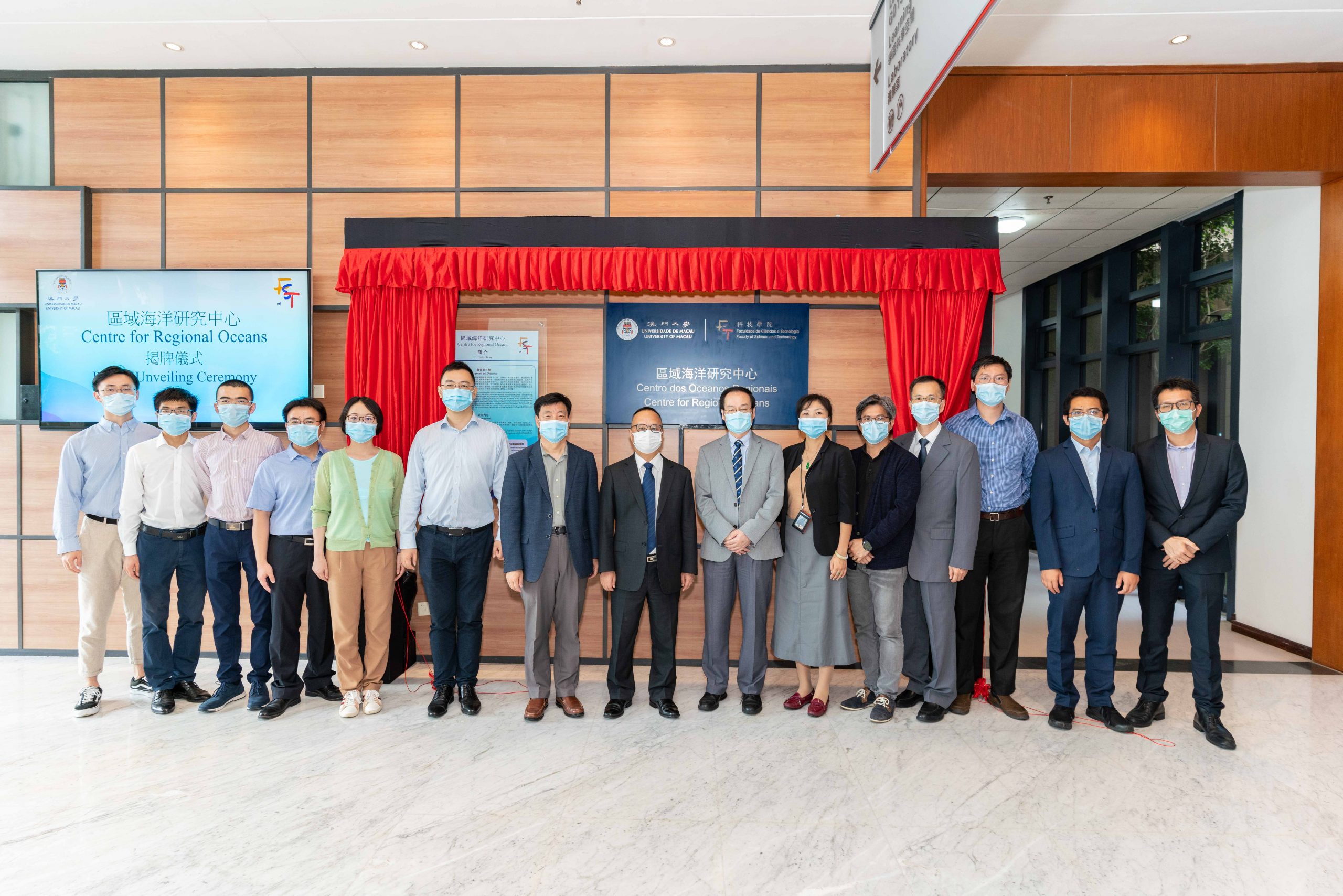
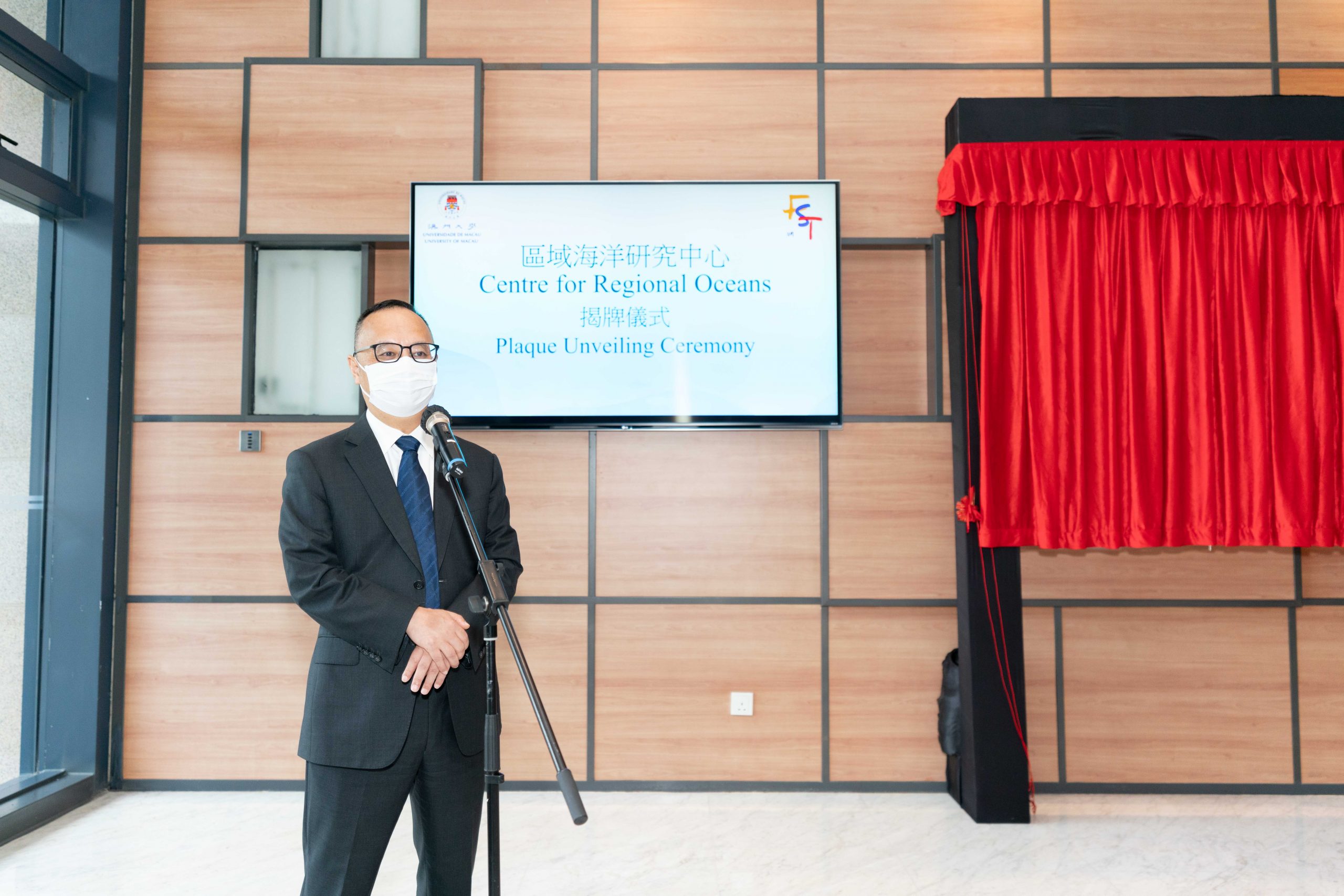
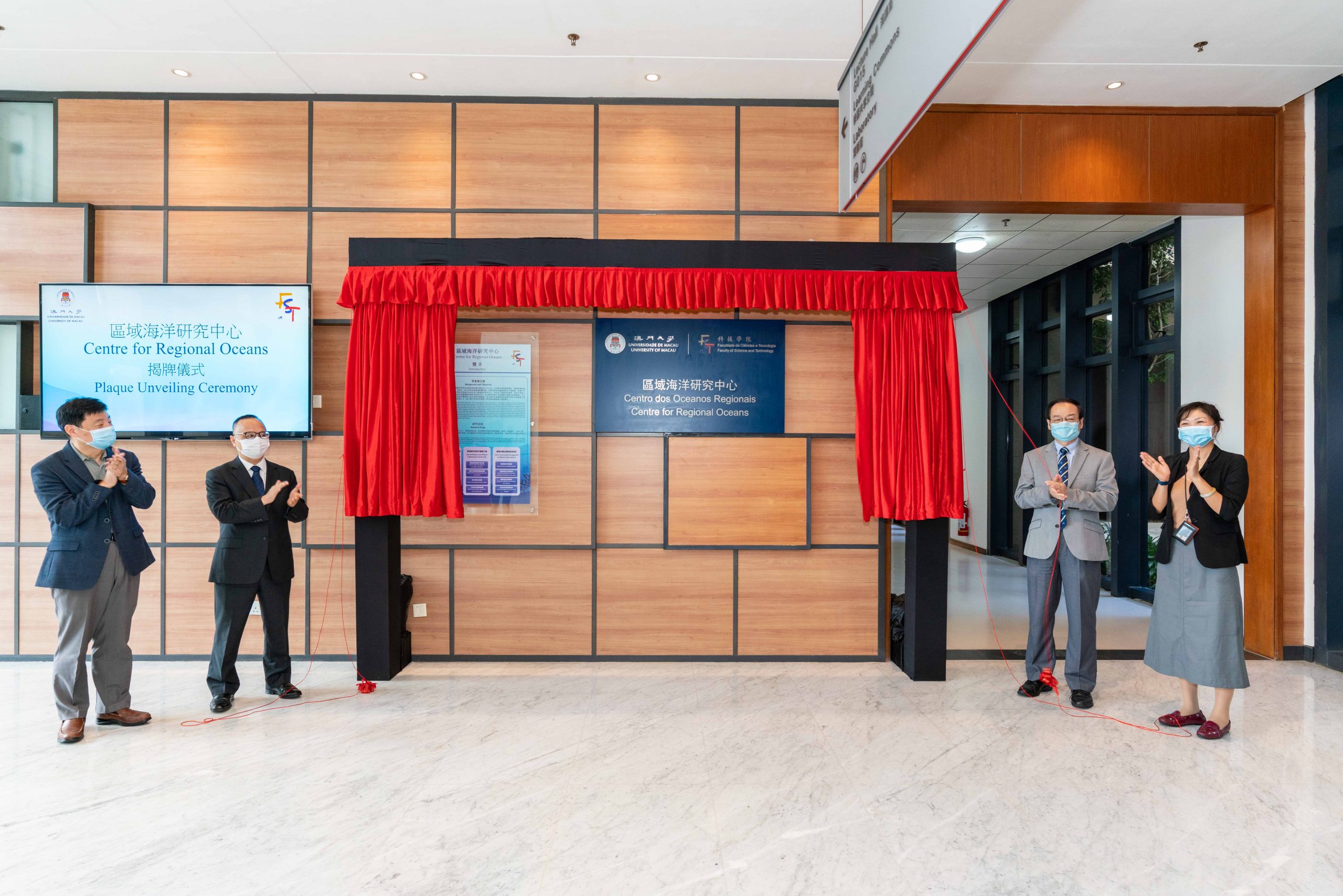
科研佈局新進展 澳大區域海洋研究中心揭牌
澳門大學科技學院的“區域海洋研究中心”舉行揭牌儀式,標誌著澳大全面推進在區域海洋領域的研究,助力澳門經濟多元發展,為粵港澳大灣區的長遠發展做出貢獻。
儀式上,澳大校長宋永華、副校長葛偉、科技學院院長須成忠和區域海洋研究中心代主任周萬歡主持揭牌。宋永華致辭時表示,面對澳門特區政府 […]
大型土木工程結構參數識別的振動傳遞比方法及其應用研究
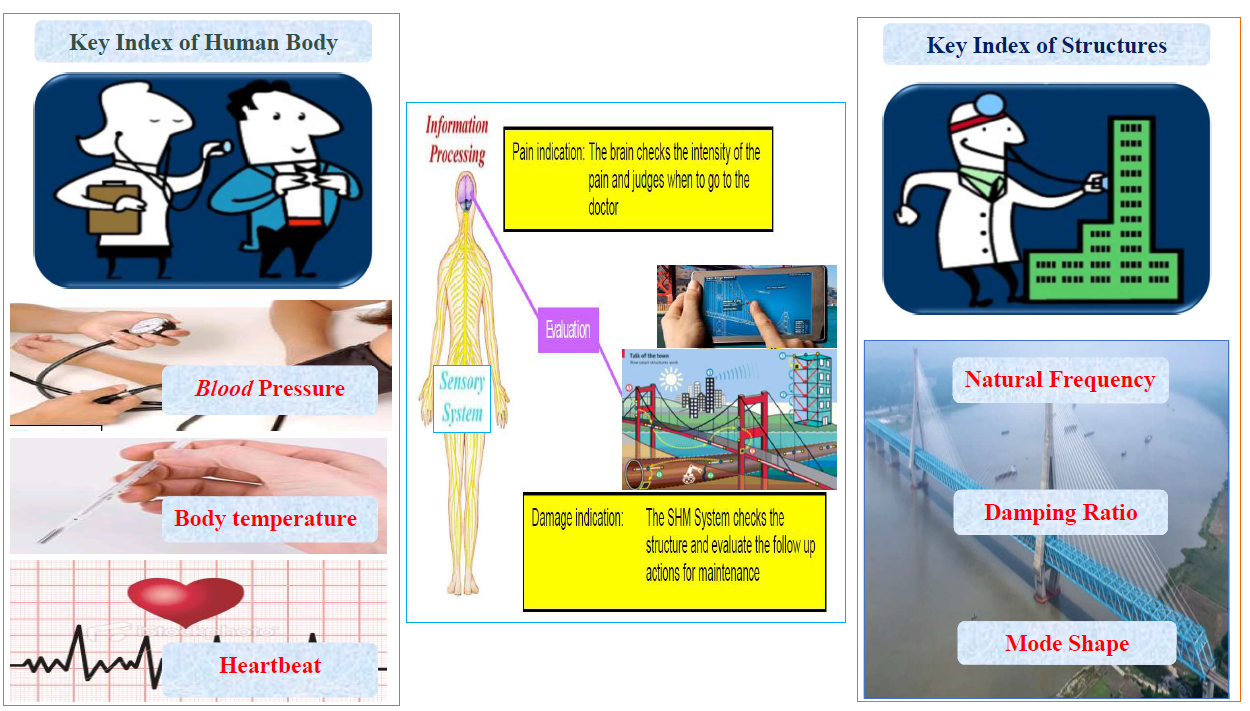
在研究工程結構動力災變機理、健康監測和安全評估時,一個首先需要解決的關鍵問題就是正確地識別或監測結構的動力特性或參數,這些參數是研究結構災變機理、健康監測和安全評估的基礎和依據。參數識別屬於系統識別範疇,一般意義上講,就是在觀察到的系統輸入(激勵)和輸出(回應)資料的基礎上,對系統確定一個數學模型,要求這個模型盡可能精確地反映系統的特性,從而達到識別系統 […]
大氣環境中的空氣質量預測和模擬
透過對大氣環境中的空氣質量進行預測和模擬,了解澳門空氣質量每日變化的規律,影響因素與機制。
To strive for the continuous improvement of the urban air quality in Macau, our researches f […]
活動預告
蘇伊士與澳門大學攜手創新研究 致力於保護海洋環境
積極拓展區域海洋環境領域的研究是澳門大學的科研戰略佈局中重要一環,藉著世界海洋日,澳大與蘇伊士及旗下澳門自來水股份有限公司宣佈簽署合作框架協議,三方通過整合各方在科研和海洋環境保護上的資源與優勢,建立高水準的科研合作平台,開展近海環境生態與水處理技術等相關領域的創新性研究,攜手保護海洋環境及豐富海洋生物多樣性。
這次合作將鞏固科研人才方面的培養和合作, 並進一步加強與葡萄牙在海洋領域的合作,推動科學與技術的研究和應用,保護及修復環境要素。三方今後科研的領域主要涵蓋:
- 控制鹹潮的線上檢測技術,減低鹹潮對澳門飲用水質的影響。
- 人工智慧與大數據技術在水質檢測的研究,如智慧水錶對居民的用水數據及漏水提醒等。
- 污水處理廠污染物處理的相關研究。
- 海洋生態與環境科學、飲用水水質以及新興污染物、飲用水水質線上監測的研究。
- 區域海洋環境與濱海建築工程開展系統、方法、技術等具體研究。
澳門三面環海,為支持澳門繁榮穩定,實現經濟社會可持續發展,中央政府於2015年將澳門特區海域面積明確為85平方公里。這裡不僅是中國一級保護動物中華白海豚重要的分佈區之一,更因鹹淡水交匯、水溫適宜而匯聚了豐富的魚類,使得澳門整個海洋生態系統的保護工作尤為重要。
這次三方合作,不僅把學科、人才、科技創新和產業化等優勢高度融合,共同打造產學研一體化的完整鏈條以整體修復海洋環境和生態系統,還冀在促進知識和經驗分享的同時,也開展國際交流,強化與葡萄牙在海洋領域的合作,以協助解決保護澳門乃至全球海洋環境和生物資源等迫切問題。
澳門大學校長宋永華表示,澳大作為澳門唯一一所國際化綜合性公立大學,致力透過科研促進社會發展,積極拓展區域海洋環境領域的研究是大學的科研戰略佈局中重要一環。2019年澳門大學科技學院成立區域海洋研究中心,深入開展海洋領域相關前沿課題研究、助力澳門社會與粵港澳大灣區的可持續發展。相信這次與蘇伊士及澳門自來水股份有限公司的戰略合作將會成為澳門產學研合作的典範。
蘇伊士亞洲地區水務首席執行官方恒業表示,這次是企業與高校的一次戰略性強強合作,意義重大,是我們在保護海洋上的強烈願望和一致理念的體現。蘇伊士集團自19世紀末以來已致力於保護和修復自然環境要素:水、土壤和空氣。集團在全球發動的‘SUEZ4Ocean’,更使其來自五大洲的9萬名員工身體力行參與其中,用實際行動守護海洋。此外,作為終結塑料垃圾全球聯盟(AEPW)的創始成員,蘇伊士聯合40多家國際企業,致力消滅環境中尤其是海洋中的塑料污染物。我深信,今天與澳門大學達成的合作,將進一步發揮澳門大學和蘇伊士在海洋環境與工程研究領域的特長優勢,以及澳門自來水35年來在中國水行業優質服務和智慧化管理方面的標杆經驗,以產學研模式的深度融合,服務澳門大灣區的高質量發展和全球海洋生態的可持續發展。
澳門大學
澳門大學成立於1981年,是粵港澳大灣區西岸地區最優秀,也是澳門特區唯一一所國際化綜合性公立大學。澳門大學在2020年泰晤士高等教育世界大學排名301-350 、亞洲大學排名37、國際化發展第九、全球年輕大學排名52。澳門大學科技學院於2019年成立區域海洋研究中心,深入開展海洋環境、海洋工程和海洋災害等領域的學術前沿課題,推進區域海洋相關課題的學術交流與合作,助力澳門社會乃至粵港澳大灣區的長遠發展。
蘇伊士
蘇伊士集團自19世紀末以來,不斷積累專業知識,通過保護人類健康並支持經濟增長,助力人們持續提高生活質量。蘇伊士及旗下90,000萬名員工遍布全球五大洲,致力於保護和修復我們的自然環境要素:水、土壤和空氣。在水務管理、固廢回收再造、土壤修復和空氣治理等方面,蘇伊士提供富有彈性的創新型解決方案,通過“智慧”城市優化市政和各行業的資源管理,提升其環境和經濟效益。集團向6,400萬人提供環境服務,生產飲用水71億立方米。蘇伊士還為經濟發展做出了積極貢獻,每年直接或間接創造了20多萬個就業崗位,作為新資源的提供者,生產了420萬噸再生原料。集團的目標是在2030年前提供100%的可持續解決方案,為我們的環境、健康和氣候帶來積極影響。蘇伊士集團2019年的總收入達180億歐元。
蘇伊士在亞洲
蘇伊士在早於60年前就進入東南亞,繼而擴展至大中華區的發展也逾40年。蘇伊士現已成為各大城市和工商客戶的首選合作夥伴,提供的水務和固廢管理解決方案,能助其優化資源管理,提升其環境和經濟效益並符合監管標準。集團旗下逾9,000名員工遍布亞洲各地,合作項目逾70個,至今已建造了460多座水處理廠和污水處理廠並向逾3,200萬人口提供水務和固廢資源管理服務。蘇伊士被公認為最具影響力的企業之一,也是環境服務行業的標杆企業。目前蘇伊士在澳門運營著中國水務行業的第一個PPP項目,在上海運營著亞洲其中一座最大的危廢處置設施,同時在泰國也運營著塑料回收再造項目。作為香港固廢處理行業的領導者,蘇伊士集團還為亞洲20個工園區提供專業的環境管理服務。
澳門自來水股份有限公司
澳門自來水股份有限公司於1935年創立,由法國蘇伊士集團和香港新創建集團有限公司組成的蘇伊士新創建有限公司於1985年購入85%股份入主澳門自來水成為主要股東,並與當時澳葡政府簽訂一項為期25年的供水專營合約。合約於2009年獲澳門特別行政區政府延長20年至2030年7月。公司以專業技術及優質服務,為澳門提供可靠安全的供水服務,保證水質符合及優於歐洲飲用水衛生標準。公司的願景是與客戶建立親切緊密的關係,為客戶、股東、員工及社會各界友好創造價值,為澳門的繁榮與發展作出貢獻。

澳大與蘇伊士開展創新研究保護海洋
科研佈局新進展 澳大區域海洋研究中心揭牌
澳門大學科技學院的“區域海洋研究中心”舉行揭牌儀式,標誌著澳大全面推進在區域海洋領域的研究,助力澳門經濟多元發展,為粵港澳大灣區的長遠發展做出貢獻。
儀式上,澳大校長宋永華、副校長葛偉、科技學院院長須成忠和區域海洋研究中心代主任周萬歡主持揭牌。宋永華致辭時表示,面對澳門特區政府於海洋利用、海洋防災減災與海洋環境保護的挑戰,澳大特意在科研戰略佈局中重點建設區域海洋新興研究領域。區域海洋研究中心的成立標誌著大學將深入展開與海洋領域相關的前沿課題研究。此舉將促進澳門與其他國家在海洋領域的交流與合作,同時幫助澳門實現經濟多元化發展,為粵港澳大灣區的長遠發展做出貢獻。
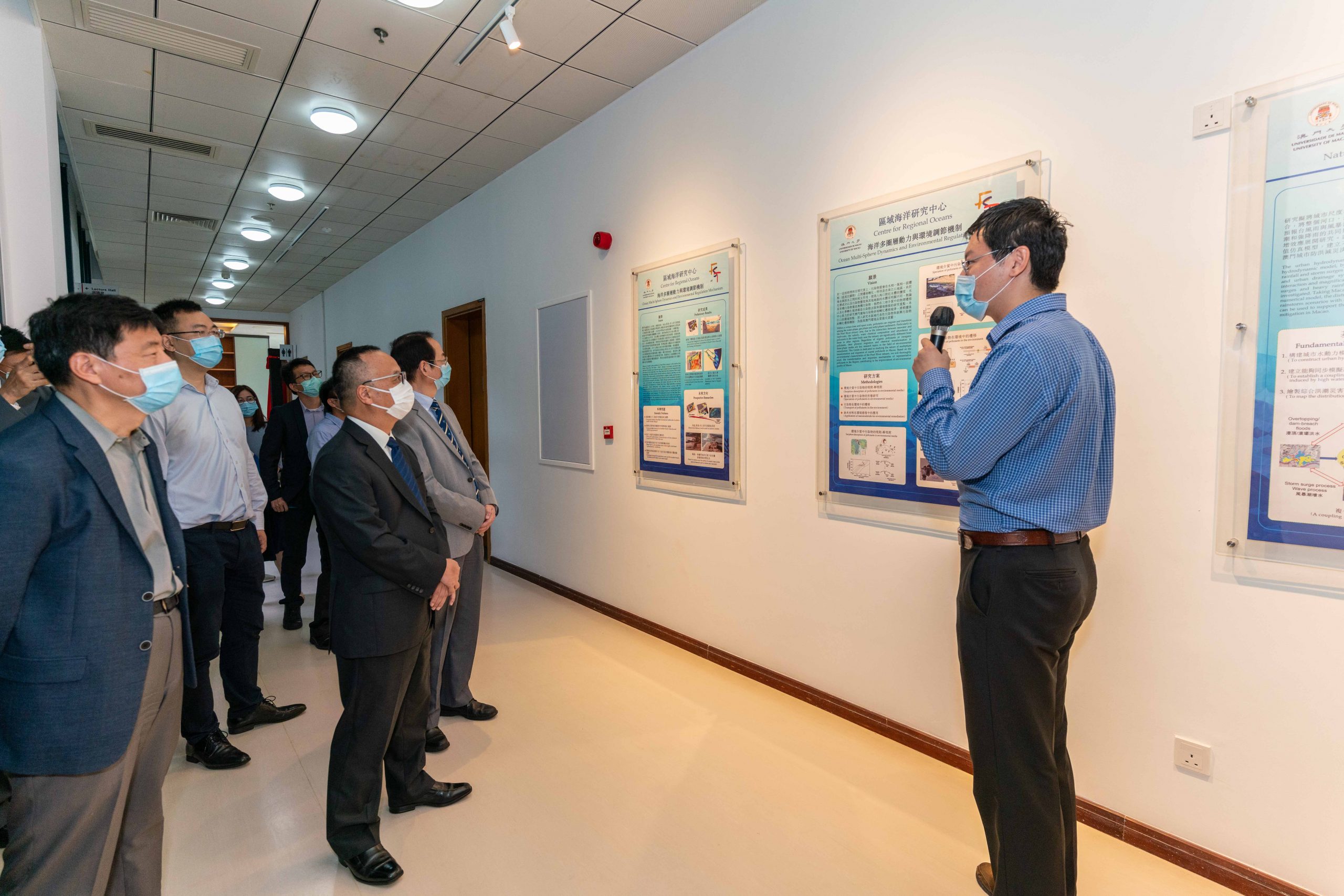
澳大區域海洋研究中心聚焦海洋多圈層動力與環境調節機制、濱海城市自然災害與工程、濱海環境治理與資源開發三個方向。周萬歡致辭時提到鑒於澳門近年先後經歷兩次風災,首要工作是解決目前海洋環境與工程方面等的科學問題,以提升澳門在海洋防災減災、海洋工程建設與維養、海洋生態環境保護、海洋資源利用等方面的水平。目前中心在相關研究領域有超過十個實驗室及多個在建實驗室,包括“海洋環境污染檢測實驗室”、“海洋環境污染防治與修復實驗室”、“海域環境污染模擬實驗室”、“環境生物技術實驗室”、“水利工程實驗室”等。
澳大區域海洋研究中心將積極貫徹落實澳大制定的“三個三”科研戰略佈局,積極拓展科技建創新平台,形成創新引領發展的新局面。“三個三”是指以三間國家重點實驗室、三個重點發展方向、三個跨學科交叉領域為骨幹的科研戰略佈局。目前,該中心已與青島海洋科學與技術試點國家實驗室、中國科學院海洋研究所、中國科學院南海海洋研究所、海洋污染國家重點實驗室、海岸和近海工程國家重點實驗室、污染控制與資源化研究國家重點實驗室等國家及大灣區頂級的海洋相關領域科研單位開展了密切合作。未來將著眼於澳門海洋科學發展所需,為澳門培養更多海洋領域專業人才,提升澳門在海洋科學領域的國際地位與影響力,為大灣區乃至國家的海洋科技發展做出貢獻。
參與儀式的嘉賓還包括:澳大研究服務及知識轉移辦公室主任楊志新教授,澳大區域海洋研究中心成員林智超教授、顏王吉教授、陸萬海教授、黎永杰教授、郝天偉教授、張平教授、施華斌教授、申平教授、高亮教授和蔡忠亞教授。





大型土木工程結構參數識別的振動傳遞比方法及其應用研究

在研究工程結構動力災變機理、健康監測和安全評估時,一個首先需要解決的關鍵問題就是正確地識別或監測結構的動力特性或參數,這些參數是研究結構災變機理、健康監測和安全評估的基礎和依據。參數識別屬於系統識別範疇,一般意義上講,就是在觀察到的系統輸入(激勵)和輸出(回應)資料的基礎上,對系統確定一個數學模型,要求這個模型盡可能精確地反映系統的特性,從而達到識別系統參數的目的。系統識別原本是現代控制理論研究的基本問題之一,近年以來已愈來愈在各類工程結構中顯示出潛在的應用前景,是學科滲透和結構工程專業概念拓寬的一個典型實例。
結構動力特性研究結構災變機理、健康監測和安全評估的基礎和依據
目前常用的結構參數識別方法通常可以分為兩類。一類是建立在系統輸入和輸出資料基礎上的識別方法。在工程結構振動試驗中, 這類方法需要測量結構的激勵(輸入)和動力回應(輸出),求出反應輸入-輸出關係和系統固有特性的傳遞函數,然後建立傳遞函數與系統參數之間的關係,從而識別出結構的特徵參數。另一類是僅建立在輸出資料基礎上的系統識別方法。這類方法直接利用車輛、行人、風荷載等作用於結構上的日常環境激勵作為系統的輸入,僅根據結構的回應資料完成參數的識別過程。為了便於數學處理,僅基於輸出資料的參數識別方法通常對輸入模型做了理想化假定。然而,這些理想化條件在實際工程中很難得到嚴格滿足,在陣風、車輛等環境荷載激勵下,很多時候工程結構難以避免地受到複雜激勵的作用,如有色雜訊激勵甚至是諧波激勵,實踐與理論的差異無疑會影響系統識別結果的魯棒性與準確性,甚至會導致識別出錯誤的結果。因此,有必要在系統識別階段引入新的方法來充分考慮輸入的影響,為土木工程結構動力災變和安全監測分析提供更穩健可靠的基礎和依據。
 |
 |
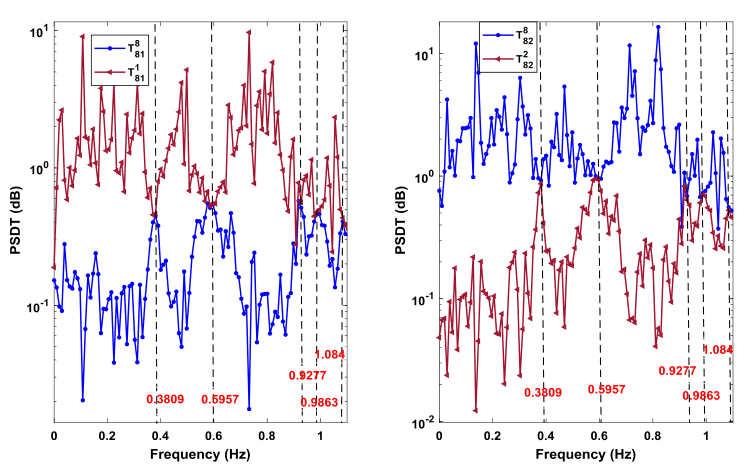
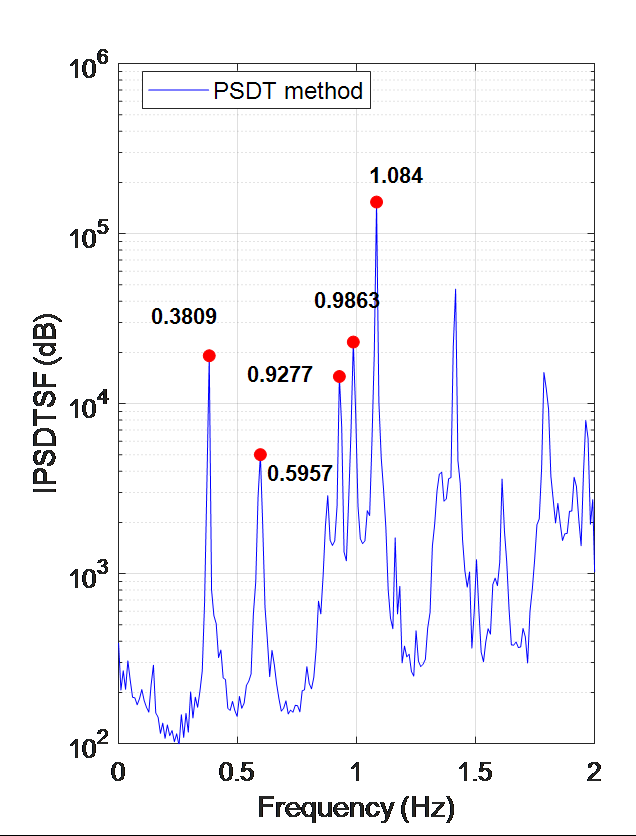
工程結構監測資料表明振動傳遞比具有獨特的物理特性和統計規律
 |
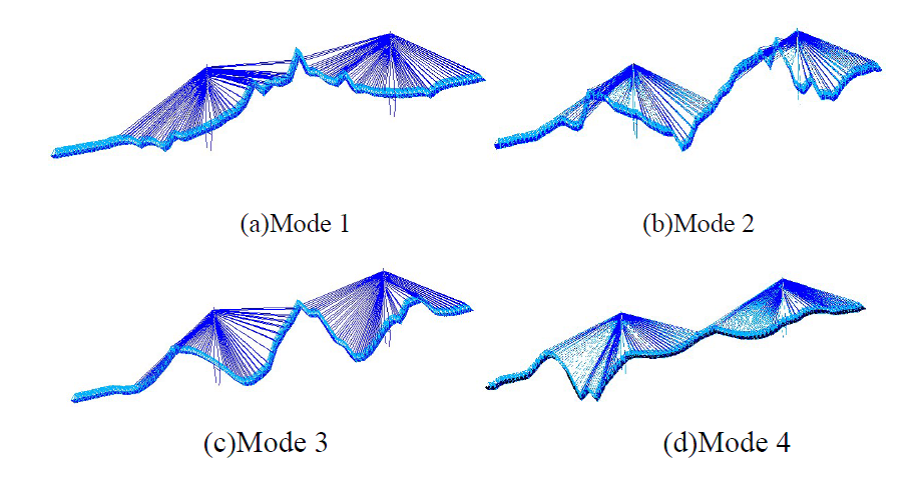 |
振動傳遞比之特性可以用於快速地識別複雜環境激勵下的結構動力特性
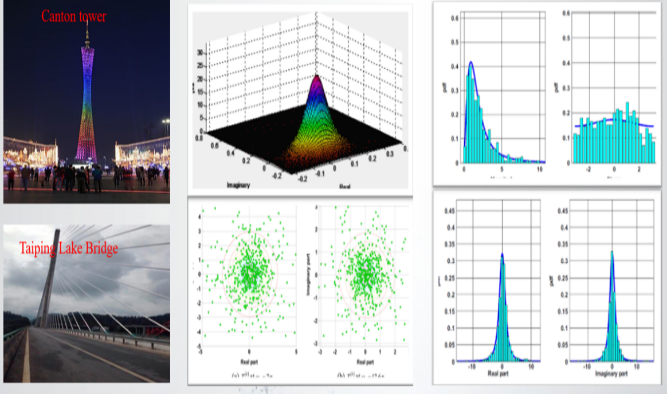
近年來,振動傳遞比函數因為其諸多優點成為了系統識別領域重要的分析手段。與頻響函數反映動力系統輸入-輸出的關係不同,振動回應傳遞比函數反映的是系統輸出-輸出之間的關係。因此,應用振動回應傳遞比函數時,系統輸入只作為動力源而不需要參與運算,因此避免了對系統荷載測量的依賴,從而有效地避免了輸入資料的測量。同時,振動回應傳遞比函數可以有效地避免對系統輸入的白色雜訊假定。通過近十餘年時間的探索,課題組在振動傳遞比的固有特性分析和參數識別方法方面取得了一系列富有創新特色的研究成果:(i)提出了功率譜傳遞比(簡稱PSDT)新概念,證明瞭複數域比例函數極限定理,揭示了PSDT在系統極點處獨立於參考輸出和激勵的位置且與兩測點的振型比值等價的物理特性;(ii)基於PSDT的物理特性,建立了PSDT驅動的結構參數識別峰值法和最小二乘複頻域方法,建立了穩定圖剔除虛假模態; (iii)證明瞭複數域比例隨機向量統計推斷定理,揭示了振動傳遞比的統計規律,建立了解析概率模型實現振動傳遞比測量不確定性表徵;(iv)基於振動傳遞比解析概率模型,提出了貝葉斯傳遞比方法實現特徵參數識別不確定性快速量化;(v)推導出了特徵參數變異係數關於不同隨機源的近似閉合解,闡明瞭不同特徵參數之間的相關程度,揭示了特徵參數不確定性的傳播機理。相關成果在國內外著名期刊發表論文12篇;曾獲省自然科學二等獎、省自然科學優秀學術論文一等獎、教育部提名國家自然科學二等獎;被澳大利亞工程院院士Hong Hao教授和上海交大國家傑青、長江彭志科教授等在內的學術同行發表的25篇論文直接跟蹤拓展,10餘篇論文在標題中直接採用了首創名詞PSDT;振動傳遞比理論在10餘座土木工程結構中得到成功應用。
相關文章
- Wang-Ji Yan and Wei-Xin Ren (2012): Operational modal parameter identification from power spectrum density transmissibility. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, Vol.27, No.3, pp.202-217.
- Wang-Ji Yan and Wei-Xin Ren (2013): Use of continuous wavelet transmissibility for operational modal identification. Journal of Structural Engineering, ASCE, Vol.139, No.9, pp.1444-1456.
- Wang-Ji Yan and Wei-Xin Ren (2015): An enhanced power spectral density transmissibility (EPSDT) approach for operational modal analysis: theoretical and experimental investigation. Engineering Structures, Vol. 102, pp.108-119.
- Wang-Ji Yan and Wei-Xin Ren (2016): Circularly-symmetric complex normal ratio distribution for scalar transmissibility functions. Part I: Fundamentals. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 80, pp.58-77.
- Wang-Ji Yan and Wei-Xin Ren (2016): Circularly-symmetric complex normal ratio distribution for scalar transmissibility functions. Part II: Probabilistic models and validation. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 80, pp.78-98.
- Wang-Ji Yan and Wei-Xin Ren (2018): Circularly-symmetric complex normal ratio distribution for scalar transmissibility functions. Part III: Application to statistical modal analysis. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 98, pp. 1000-1019.
- Wang-Ji Yan, Meng-Yun Zhao, Qian Sun and Wei-Xin Ren (2019): Transmissibility-based system identification for structural health monitoring: Fundamentals, approaches and applications. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 117, pp. 453-482.
- Wang-Ji Yan and Lambros Katafygiotis (2019): An analytical investigation into the propagation properties of uncertainty in a two-stage fast Bayesian spectral density approach for ambient modal analysis. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 118, pp. 503-533.
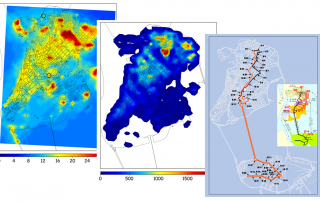
大氣環境中的空氣質量預測和模擬
透過對大氣環境中的空氣質量進行預測和模擬,了解澳門空氣質量每日變化的規律,影響因素與機制。

To strive for the continuous improvement of the urban air quality in Macau, our researches focus on two aspects, i.e., the ambient air quality forecasting and modelling. Following examples are some recent research outcomes:
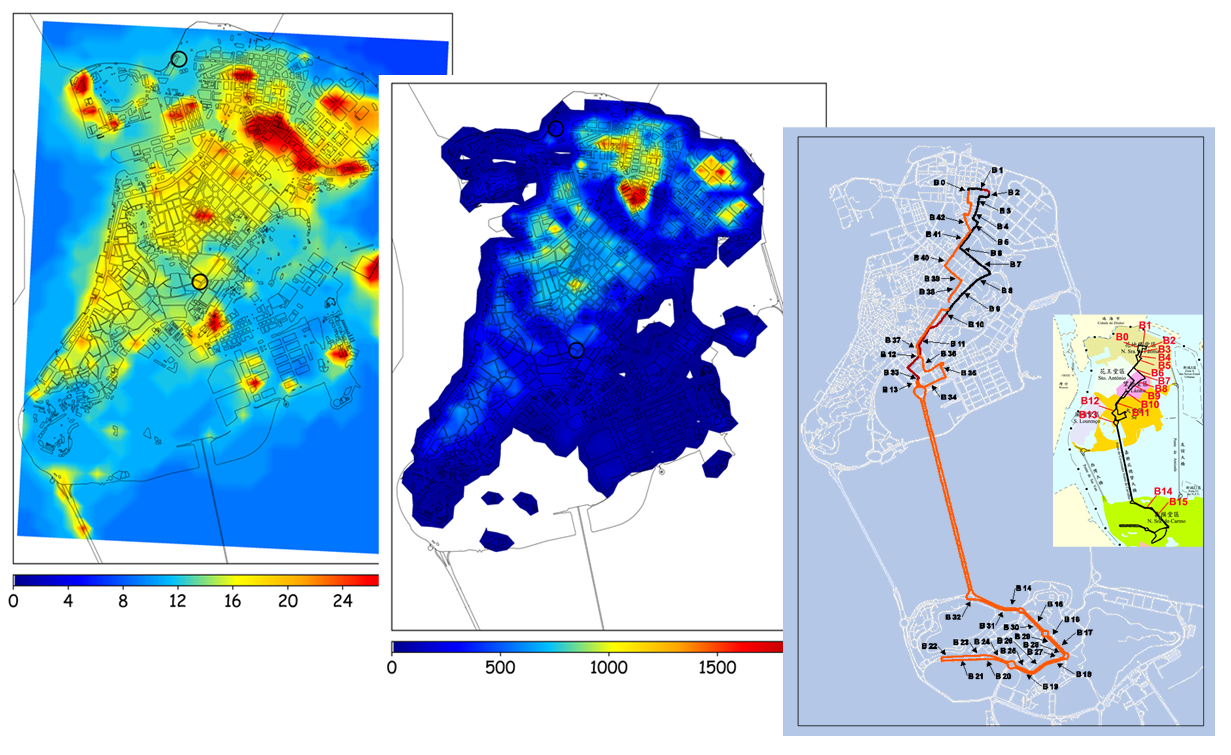
Development of a statistical forecasting model for PM2.5 in Macau based on clustering of backward air mass trajectories
Macau is a small coastal city (~30.8 km2) in the southwestern side of the Greater Bay Area. Due to its small geographical area, statistical modelling techniques are more computationally efficient and require less input information for fulfilling the purpose of operational air quality forecasting. During the model development, it is convenient to reflect the influence of local emissions and dispersion on the air quality within the city. However, it is difficult to include the effects of transboundary pollution since there is limited information addressing the transporting pathways to Macau from various source regions. Simply speaking, the source of transboundary pollution to Macau is not known. Therefore, this study attempted to address this issue in the daily forecasting model of PM2.5 in Macau by using the clustered backward air mass trajectories of HYSPLIT from 2015 to 2017. The cluster based forecasting model was found to be more efficient (~11% improvement in the critical success index) in capturing the pollution episodes compared to the ordinary model.
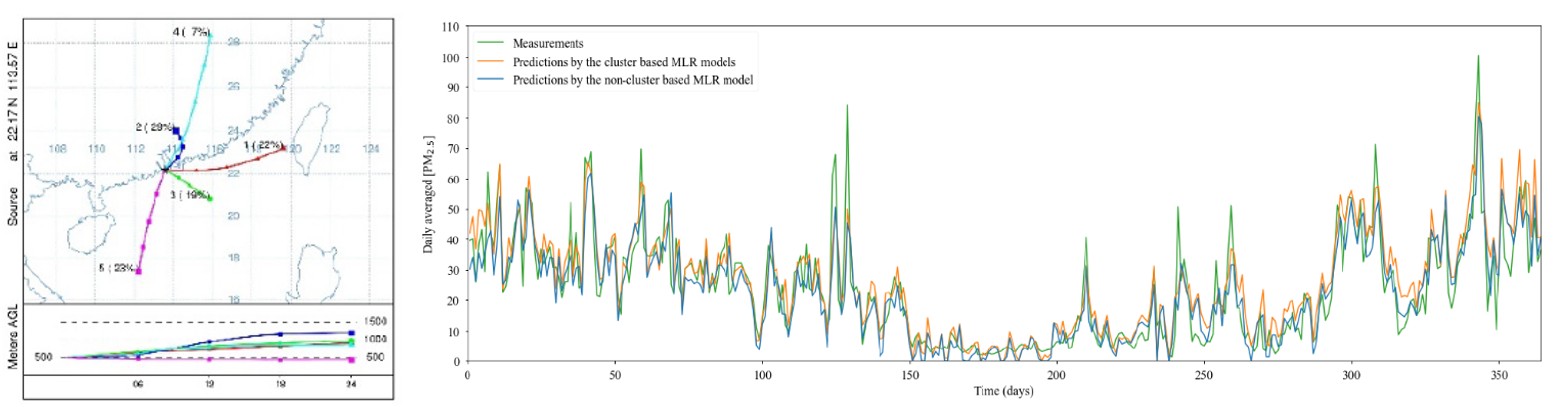
Cluster based forecasting model of PM2.5 was found to be more efficient in capturing the pollution episodes compared to the ordinary model
Predicting ground-level ozone concentrations by adaptive Bayesian model averaging of statistical seasonal models
Apart from PM2.5, the ground-level ozone is another major air pollutant of Macau or other cities in the Greater Bay Area. It is a secondary pollutant formed by the photochemical reaction of the ozone precursors (NOx, VOC). The daily variation of this pollutant has strong seasonal cycle throughout the entire year, meaning that it may not be completely described by a single model. Therefore, this study addressed the problem by proposing three ozone prediction models in different periods of the year (ozone season, non-ozone season, and the transitional period). However, sudden switching of models to their designated period in annual forecasting system may affect their performance, especially starting and ending dates of the transitional period can vary yearly. Therefore, the present study also addressed the second problem by using the adaptive Bayesian model averaging scheme. This scheme continuously evaluates the probabilities of all ozone prediction models based on the most recent ozone level. Then, the predicted ozone concentration by this scheme is obtained from the weighed sum of the model outputs according to their probabilities. Based on the measured ozone concentrations at the Taipa ambient station of the Macau Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau, results were proved to be satisfactory.
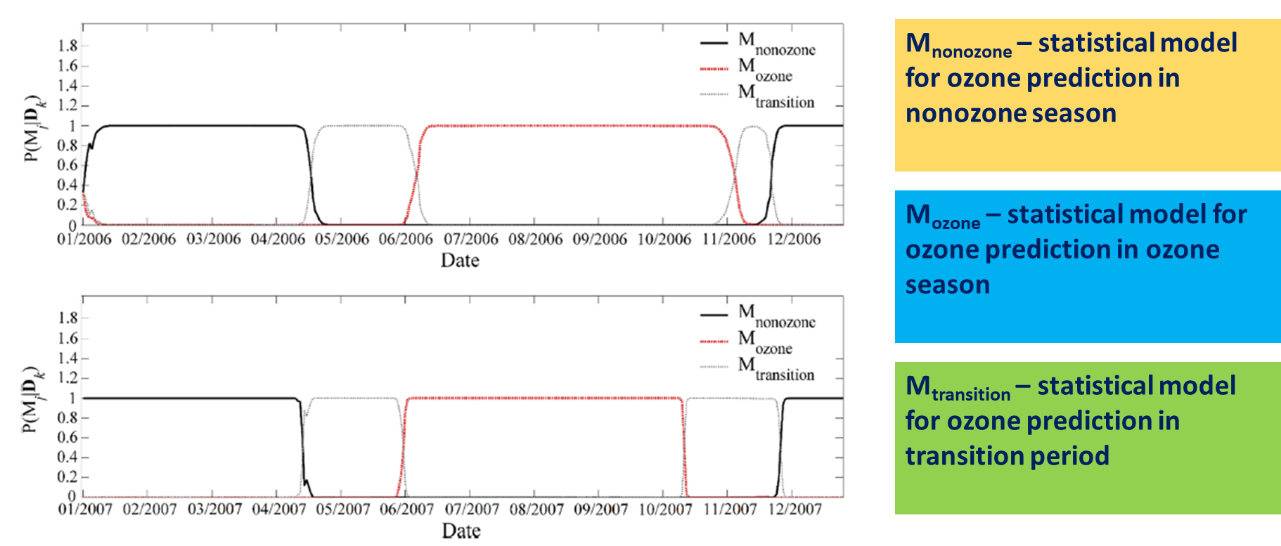
Adaptive Bayesian Model Averaging Scheme to perform averaging of ozone predictions from several models for DMA8 based on the conditional probability of each model throughout the year.
Bias correction of deterministic air quality model WRF-EURAD
The deterministic air quality model, which is the combination of the meteorological model and the chemical transport model, is widely accepted as the tool to perform operational air quality forecasting due to the large spatial coverage and its ability to explain the mechanism of the predicted pollution episodes (e.g. land-sea breeze, cold front, tropical cyclone, etc.). However, the accuracy of prediction relies on precise input information such as land cover, emission inventories, initial & boundary conditions from the global scale model, etc. Therefore, the accumulation of these uncertainties usually leads to the forecast bias. Empirical correction of the model output based on the measured pollutant concentration at the monitoring station (a.k.a. bias correction) is commonly used for improving the forecast performance. The present study attempted to develop an adaptive bias correction model by using a two-stage approach. First, a systematic selection of the most plausible bias correction model among the candidates was carried out by using the Bayesian model selection approach. Then, the Kalman filter was further implemented onto the selected model in order to transform it into an adaptive bias correction model. The two-stage approach was applied to the case study which corrects the model output of WRF-EURAD for one-day ahead prediction of PM10 concentration in Porto, Portugal. Based on the training data, the selected model at each station was found to have significantly higher probability than the other candidates, and it is also much simpler than the full model. As for the evaluation period, the corrected forecasts by the adaptive bias correction model show significant improvement over the raw outputs of WRF-EURAD. The results confirmed the success of the proposed technique.
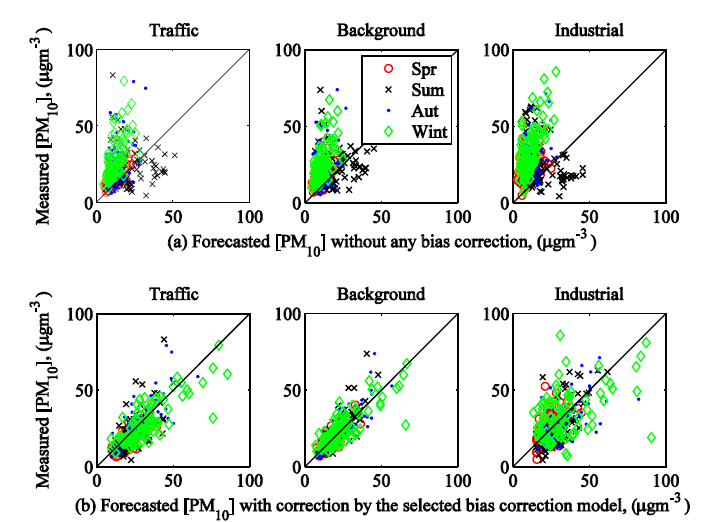
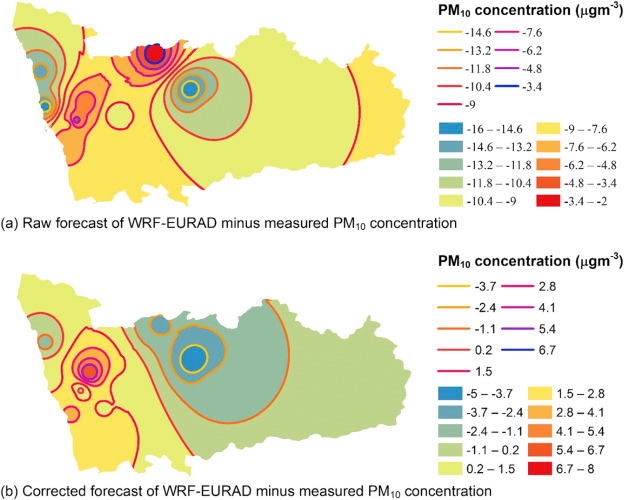
Implementation of the Kalman filter on the selected bias correction model can significantly reduce the forecast bias of PM10 concentrations in Porto, Portugal
ALL-IN-ONE Air quality modelling system applied to Macau
Air quality is one of the main environmental concerns by the Macau citizens in recent years. This region is highly affected by the pollution of respirable particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5). The sources of PM comprise of the local anthropogenic sources (road, maritime and air transport as well as domestic, industries and construction activities) and the external influence of air pollution from its neighboring regions. Notwithstanding the potential use of air quality modelling to provide scientific advice on atmospheric emission reduction strategies, air quality forecast, air pollution assessment and air quality regulations at several spatial scales, there are only few air quality modelling applications over the Macau SAR. This study designed a multi-scale air pollution modelling system (ALL-IN-ONE) to provide scientific advice to the policy makers in their strategic planning to improve the air quality and to assess the PM pollution phenomena over Macau. The ALL-IN-ONE is based on the selection of a set of models able to reproduce the meteorological and air quality patterns, from regional to local scales. The system revealed a good performance for meteorological and air quality modelling simulations. From the modelling results, it was found that Macau was affected by air pollution transport from the neighboring regions and population was exposed to the high PM levels over entire study area. Although the tested reduction scenarios of local sources showed a reduction of PM level, several exceedances of daily concentrations were still observed. Therefore, it is necessary to join efforts with neighboring regions to discuss/apply air pollution reduction measures in order to improve the air quality of Macau. The results of this work demonstrated the importance of integrated use of modelling tools to study air pollution phenomena over Macau (ranging from regional to local scales) to define efficient air quality management strategies.
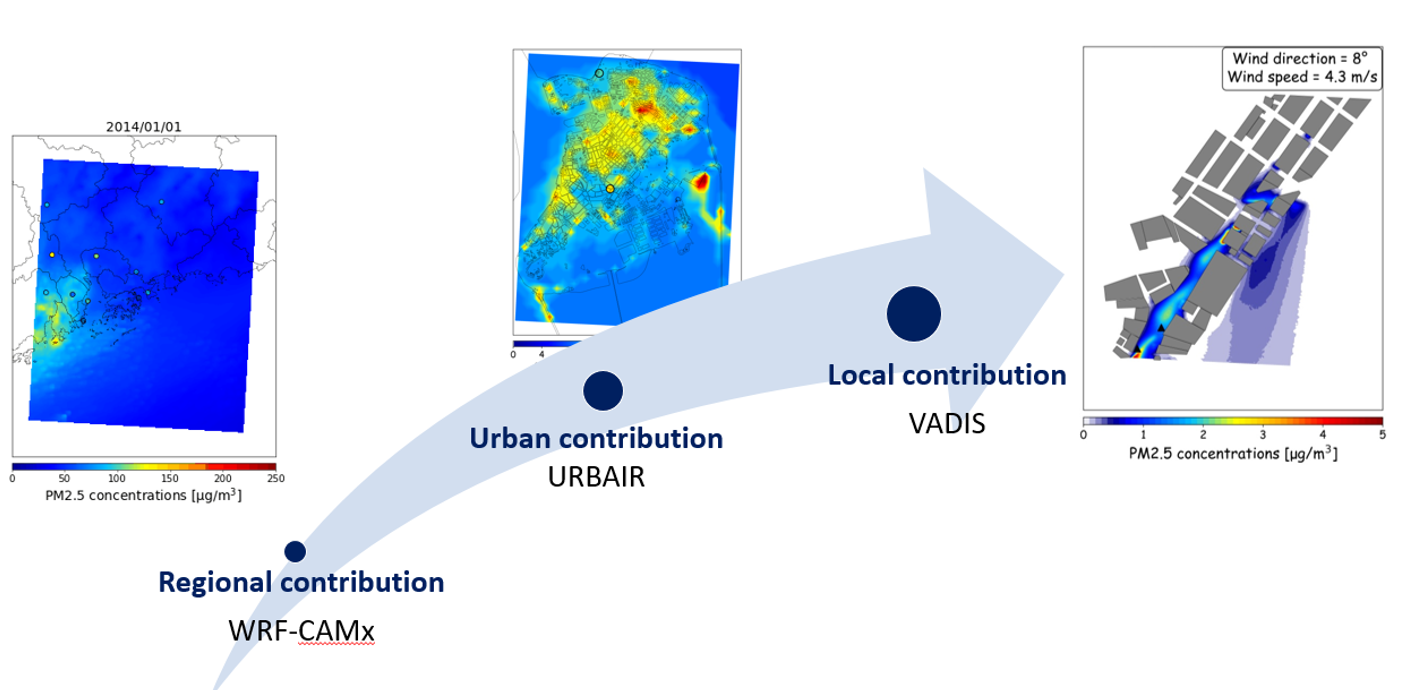
ALL-IN-ONE is an integrated modelling system addressing the contribution of air pollution of Macau from regional scale, urban scale to local scale
相關文章
- Li, X., Lopes, D., Mok, K.M., Miranda, A.I., Yuen, K.V. and Hoi K.I. (2019) Development of a road traffic emission inventory with high spatial-temporal resolution in the world’s most densely populated region-Macau, Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, Vol. 191(4), 239 | DOI: 10.1007/s10661-019-7364-9
- Lopes, D., Ferreira, J., Hoi, K.I., Miranda, A.I., Yuen, K.V. and Mok K.M. (2019) Weather Research and Forecasting Model Simulations over the Pearl River Delta Region, Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, Vol. 12(1), 115-125.
- Liu, B., He, M.M., Wu, C., Li, J., Li, Y., Lau, N.T., Yu, J.Z., Lau, A.K.H., Fung, J.C.H., Hoi, K.I., Mok, K.M., Chan, C.K., Li, Y.J. (2019) Potential Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Black Carbon on Jogging Trails in Macau, Atmospheric Environment, Vol. 198, 23-33.
- Mok, K.M., Yuen, K.V., Hoi, K.I., Chao, K.M. and Lopes, D. (2018) Predicting Ground-level Ozone Concentrations by Adaptive Bayesian Model Averaging of Statistical Seasonal Models, Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, Vol. 32(5), 1283–1297.
- Hoi K. I., Mok, K. M., Miranda, A.I., Yuen, K. V., Monteiro, A., Ribeiro, I., and Lopes, D. (2018). 利用簡約函數形式對數值空氣品質預報系統進行自我調整偏差修正, 兩岸四地環境科技創新與合作青年學者論壇, August 4, Hefei, China.
- Lopes, D., Ferreira, J., Yuen, K.V., Borrego, C., Hoi, K.I., Miranda, A.I. and Mok, K.M. (2018) Desenvolvimento de um Sistema Multi-Escala de Modelação da Qualidade do ar sobre a Região Administrativa Especial de Macau, CIALP – 1º Conferência Internacional de Ambiente em Língua Portuguesa, 8-10 May, Aveiro, Portugal.
- Liu, B., He, M.M., Hoi, K.I., Mok, K.M. and Li, Y.J. (2017) Potential Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Black Carbon on Jogging Trails in Macau, Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Regional Air Quality Management in Rapidly Developing Economic Regions, 16-19 November, Guangzhou, China.
- Mok, K.M., Miranda, A.I., Yuen, K.V., Hoi, K.I., Monteiro, A. and Ribeiro, I. (2017) Selection of Bias Correction Models for Improving the Daily PM10 Forecasts of WRF-EURAD in Porto, Portugal, Atmospheric Pollution Research, Vol. 8(4), 628-639.
- Hoi, K.I., Chio, C.W., Lopes D., and Mok, K.M. (2017) Seasonal Difference of PM10 Exposure in a Diesel Bus, The 5th International Symposium on Regional Air Quality Management in Rapidly Developing Economic Regions, 16-19 November, Guangzhou, China.
- Lopes, D., Hoi, K.I., Mok, K. M., Miranda, A.I., Yuen, K. V. and Borrego, C. (2016) Air Quality in the Main Cities of the Pearl River Delta Region, Global NEST Journal, Vol. 18, no.4, 794 – 802.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V., Mok, K. M., Miranda, A.I. and Ribeiro, I. (2016), Comparison of the Offline and the Online Bias Correction of the WRF-EURAD in Porto, Portugal. In: S. Sauvage, J.M. Sánchez-Pérez & A.E. Rizzoli, (Eds.), Proceedings of the 8th International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software, July 10-14, Toulouse, France, Vol. 2, 377 – 383.
- Lopes, D., Ferreira, J. Hoi, K. I., Mok, K. M., Miranda, A. I. and Yuen, K. V. (2016), WRF-CAMx Application to the Pearl River Delta Region, Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes (HARMO 17), May 9-12, Budapest, Hungary, 121-125.
- Lopes D., Hoi K.I., Mok K.M., Miranda A.I., Yuen K.V., Borrego C. (2015). State of the Air Quality in the Main Regions of Pearl River Delta. Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, September 3-5, Rhodes, Greece, 5pp.
- Mok, K. M., Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V., Miranda, A. I., Borrego, C. and Ribeiro, I. (2015) Selection of a Parsimonious Empirical Correction Rule for a Deterministic Air Quality Model, 2015 International Conference on Earth Observations & Societal Impacts and ICLEI Resilience Forum, June 28 – 30, Kaohsiung, Taiwan. (Session Keynote)
- Hoi, K.I., Zhang, D.B., Mok, K.M.and Yuen, K.V. (2014) Association of Human Mortality with Air Pollution of Hong Kong, Toxics, Vol. 2, 158 – 164.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V., Mok, K. M., Miranda, A. I. and Lai, K. U.(2014) Selection of the Daily PM10 Forecasting Model for an Urban Area in the Northern Region of Portugal with the Bayesian Approach, 2014 International Aerosol Conference, Aug. 28 – Sept. 2, Busan, Korea.
- Hoi, K.I., Yuen, K.V. and Mok, K. M. (2013) Improvement of the Multilayer Perceptron for Air Quality Modelling through an Adaptive Learning Scheme, Computers & Geosciences, Vol. 59, 148 – 155.
- Hoi, K. I., Mok, K. M., Yuen, K. V. and Pun, M. H. (2013) Investigation of Fine Particulate Pollution in a Coastal City with a Mobile Monitoring Platform, Global NEST Journal, Vol. 15, no.2, 178 – 187.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2013) Bayesian Model Class Selection of Daily Ground-level Ozone Prediction Model, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Environmental Management, Engineering, Planning and Economics (CEMEPE) and SECOTOX Conference, June 24-28, Mykonos Island, Greece, 425 – 431.
- Chao, K.M., Hoi, K.I., Yuen, K.V. and Mok, K.M. (2012) Adaptive Modelling of the Daily Behavior of the Boundary Layer Ozone in Macau. ISRN Meteorology, Vol. 2012, Article ID 434176, 7 pages. doi:10.5402/2012/434176.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V., and Mok, K. M. (2011) Iterative Probabilistic Approach for Selection of Time-varying Model Classes, Procedia Engineering, 14, 2585 – 2592.
- Hoi, K. I., Mok, K. M., Yuen, K. V. and Pun, M. H. (2011) Assessment of Fine Particulate Pollution in Macau Using a Mobile Monitoring Platform, Proceedings of the 12th International Conference for Environmental Science and Technology, September 8-10, 2011, Rhodes Island, Greece, A, 737-744.
- Hoi, K.I., Yuen, K.V. and Mok, K.M. (2010) Optimizing the Performance of Kalman Filter Based Statistical Time-varying Air Quality Models. Global NEST Journal, Vol. 12, no.1, 27 – 39.
- Hoi, K.I., Mok, K.M., Yuen, K.V., Pun, M.H., Cheng, A.Y.S., Visue, A. and Vong M.H. (2010) Spatial and temporal variation of black carbon pollution in a coastal city accessed using a mobile monitoring platform, Urban Environmental Pollution: Overcoming Obstacles to Sustainability and Quality of Life (UEP2010), 20-23 June 2010, Boston, USA, P1.20.
- Pun, M.H., Hoi, K.I., Mok, K.M., Yuen, K.V., Cheng, A.Y.S., Visue, A. and Vong M.H. (2010) Transforming the WPS measurements from a mobile monitoring platform into PM10 mass concentrations for city air quality assessment, Urban Environmental Pollution: Overcoming Obstacles to Sustainability and Quality of Life (UEP2010), 20-23 June 2010, Boston, USA P1.38.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V., and Mok, K. M. (2010) Is a Complex Neural Network Based Air Quality Prediction Model Better Than a Simple One? A Bayesian Point of View, Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Computational Mechanics in conjunction with the 12th International Conference on the Enhancement and Promotion of Computational Methods in Engineering and Science, Ed. by Lu, J.W.Z., Leung, A.Y.T., Iu, V.P. & Mok, K.M., American Institute of Physics, Melville, NY, Part I, 764 – 769.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2009) Prediction of Daily Averaged PM10 Concentrations by Statistical Time-varying Model, Atmospheric Environment, 43, issue 16, 2579-2581.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2009) Enhancement of Kalman Filter Based Air Quality Predictive System by Using Bayesian Approach, Proceedings of the 11th International Conference for Environmental Science and Technology, September 3-5, 2009, Chania, Crete, Greece, A, 457-466.
- Mok, K. M., Miranda, A. I., Leong, K. U and Borrego, C. (2008) A Gaussian Puff Model with Optimal Interpolation for Air Pollution Modelling, International Journal of Environment and Pollution, Vol. 35, no. 1, 111–137.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2008) Kalman Filter Based Prediction System for Wintertime PM10 Concentrations in Macau, Global NEST Journal, 10, no.2, 140–150.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2008) Time-varying Models for Forecasting Summertime Daily Averaged PM10 Concentrations of Macau, Proceedings of the1st Nanshan District Academic Forum of PhD Candidates’ from Shenzhen, Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan in conjunction with the196th Tsinghua Forum for Doctoral Candidates, November 28-29, 2008,Shenzhen, China, 10pp. (Second Prize of the Best Paper Award)
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2008) An Artificial Neural Network Model for the Prediction of Daily Averaged PM10 Concentrations in Macau, Proceedings of the 6th National Civil Engineering Forum for Graduate Students, November 22-23, 2008, Beijing, China.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2007) Statistical Modeling of PM10 concentrations in Macau by using Kalman filter, Proceedings of the APCOM’07 in conjunction with EPMESC XI (CD-ROM), December 3-6, 2007, Kyoto, Japan, MS41-4-4, 9pp.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2007) Applying Kalman Filter to Forecast Short-term Air Quality in Macau, Proceedings of the 10th International Conference for Environmental Science and Technology, September 5-7, 2007, COS Island, Greece, Vol. A, 504-511.
- Chang, S. W., Mok, K. M. and Yuen, K. V. (2007) Association of PM10 Pollution Episodes with the Meterological Conditions in Macau, Proceedings of the 10th International Conference for Environmental Science and Technology, September 5-7, 2007, COS Island, Greece, Vol. B, 90-95.
- Yuen, K. V., Hoi K. I., and Mok, K. M. (2007) On the Selection of Noise Parameters for Kalman Filter, Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, Vol. 6, no. 1, 49 – 56.
- Hoi K. I., Mok K. M., and Yuen K.-V. (2006) Analysis of Wet Acid Deposition in Macau, Global NEST Journal, Vol. 8, no.3, 224 – 233.
- Hoi K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2006) Updating Noise Parameters of Kalman Filter Using Bayesian Approach, Computational Methods in Engineering & Science: Proceedings of the EPMESC X, by Yao, Z.H., Yuan, M.W. & Chen, Y.Q., Tsinghua University Press & Springer, Beijing, 782 – 791. (EPMESC X Student Paper Competition Award)
- Lam, L. H. and Mok, K. M. (2006) Prediction of PM10 Concentrations in Macao with Artificial Neural Network, Computational Methods in Engineering & Science: Proceedings of the EPMESC X, Ed. by Yao, Z.H., Yuan, M.W. & Chen, Y.Q., Tsinghua University Press & Springer, Beijing, 895 – 902.
- Mok, K.M. , Hoi, K.I. and Yuen K.V. (2005) Causes of Wet Acid Deposition in Macau, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, September 1 – 3, 2005, Rhodes island, Greece, Vol. B, 623-628.
- Mok, K. M. and Hoi, K. I. (2005) Effects of Meteorological Conditions on PM10 Concentrations – A Study in Macau, Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, Vol. 102, 201-223.
- Tsai, W. Y., Chan, L. Y., Chan, C. Y., Wong, K. H. and Mok, K. M. (2004) Respirable Suspended Particulate in Macao, The 3rd Asian Aerosol Conference, January 6 – 9, 2004, Hong Kong, (Fri-B2, OAA05).
- Mok, K. M. and Hoi, K. I. (2003) Association of PM10 Concentrations and Wind Directions in Macau, Proceedings of the International Conference on Pollution in Metropolitan and Urban Environment – POLMET 2003 (POLMET CD Rom), Nov. 3-5, 2003, Hong Kong, Session 6A, 6pages.
- Chan, L. Y., Wong, K. H., Chan, C. Y., Tsai, W. Y. and Mok, K. M. (2002) Carbon Monoxide in Urban Roadside Microenvironments of Macao, Proceedings of the Regional Workshop on Better Air Quality in Asian and Pacific Rim Cities (BAQ 2002 CD Rom), Hong Kong, PS-34-1 – PS-34-4.
- Mok, K. M. (2002) Development of an Air-Quality Index Forecasting System for Macau – A Memoir, Investigação Científica Sobre o Ambiente e Desenvolvimento Urbano em Macau, Ed. by Wang, Z.S., Chen, J.N., & Du, P.F., Univ. of Macau, Tsinghua Univ. & National Natural Science Foundation, Macau, 34-46. (Invited Lecture)
- Mok, K. M., Tam, S. C., Hoi, K. I. and Lei, S. I. (2002) Um Sistema “Inteligente” de Previsão da Qualidade do ar em Macau, Revista do Ambiente, ANO 6, No. 20-21, 92-96.
- Mok, K. M., Tam, S. C., Hoi, K. I. and Lei, S. I. (2002) An Intelligent Air-Quality Forecasting System in Macao, Proceedings of the 2001 International Conference and Exhibition on Sustainable Development and Green Enterprises, Ed. By Environment Council, Macao Special Administrative Region, P.R. China, Environment Council, 273-282. (Invited Lecture)
- Mok, K. M., Tam, S. C., Yan, P. and Lam, L. H. (2000) A Neural Network Forecasting System for Daily Air Quality Index in Macau, Air Pollution VIII, Ed. by Longhurst, J.W.S., Brebbia, C.A., & Power, H., WIT Press, Southampton, 41-50.
- Mok, K. M., Tam, S. C. and Wang, Z. S. (1999) Air-Quality Forecasting System in Macau, Proceedings of the 1st Macau Symposium on Environment and City Development, Macau, 78-85.
- Mok, K. M., Tam, S. C., Lam, L. H., and Yan, P. (1999) Prediction of Macau Daily Electricity Consumption with Artificial Neural Network, Computational Methods in Engineering and Science – EPMESC VII, Ed. by Bento, J., Oliveira, E. A. & Pereira, E., Elsevier Science, Kidlington, Oxford, Vol. 2, 827 – 836.
- Tam, S. C., Mok, K. M., Yan, P., and Lam, L. H. (1999) An Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System for the Forecast of Macau Daily Electric Load, Computational Methods in Engineering and Science – EPMESC VII, Ed. by Bento, J., Oliveira, E. A. & Pereira, E., Elsevier Science, Kidlington, Oxford, Vol. 2, 817 – 826.
- Mok, K. M. (1998) INTELAIR-Hybrid System for Urban Air Pollution Management: Artificially Intelligent and Traditional Modelling, Proceedings of S&T Co-Operation with Asia in the Area of Sustainable Management of Natural Resource – A Co-Ordination Meeting in China (CD-ROM), Ed. by J. P. Lobo-Ferreira and Tilak Viegas, CEC-DGXII-INCO-DC and P.R. China-SSTC-DIC. (Invited Presentation)
- Mok, K. M. and Tam, S. C., (1998) Short-Term Prediction of SO2 Concentration in Macau with Artificial Neural Networks, Energy and Buildings, Vol. 28, 279-286.
- Tam, S. C., Mok, K. M. and Sam, C. (1998) Adaptive Fuzzy System for Prediction of SO2 concentration in Macau, Air Pollution VI, Ed. by Brebbia, C.A., Ratto, C.F. & Power, H., WIT Press/Computational Mechanics Publications, Southampton, 277-286.
過去活動
蘇伊士與澳門大學攜手創新研究 致力於保護海洋環境
積極拓展區域海洋環境領域的研究是澳門大學的科研戰略佈局中重要一環,藉著世界海洋日,澳大與蘇伊士及旗下澳門自來水股份有限公司宣佈簽署合作框架協議,三方通過整合各方在科研和海洋環境保護上的資源與優勢,建立高水準的科研合作平台,開展近海環境生態與水處理技術等相關領域的創新性研究,攜手保護海洋環境及豐富海洋生物多樣性。
這次合作將鞏固科研人才方面的培養和合作, 並進一步加強與葡萄牙在海洋領域的合作,推動科學與技術的研究和應用,保護及修復環境要素。三方今後科研的領域主要涵蓋:
- 控制鹹潮的線上檢測技術,減低鹹潮對澳門飲用水質的影響。
- 人工智慧與大數據技術在水質檢測的研究,如智慧水錶對居民的用水數據及漏水提醒等。
- 污水處理廠污染物處理的相關研究。
- 海洋生態與環境科學、飲用水水質以及新興污染物、飲用水水質線上監測的研究。
- 區域海洋環境與濱海建築工程開展系統、方法、技術等具體研究。
澳門三面環海,為支持澳門繁榮穩定,實現經濟社會可持續發展,中央政府於2015年將澳門特區海域面積明確為85平方公里。這裡不僅是中國一級保護動物中華白海豚重要的分佈區之一,更因鹹淡水交匯、水溫適宜而匯聚了豐富的魚類,使得澳門整個海洋生態系統的保護工作尤為重要。
這次三方合作,不僅把學科、人才、科技創新和產業化等優勢高度融合,共同打造產學研一體化的完整鏈條以整體修復海洋環境和生態系統,還冀在促進知識和經驗分享的同時,也開展國際交流,強化與葡萄牙在海洋領域的合作,以協助解決保護澳門乃至全球海洋環境和生物資源等迫切問題。
澳門大學校長宋永華表示,澳大作為澳門唯一一所國際化綜合性公立大學,致力透過科研促進社會發展,積極拓展區域海洋環境領域的研究是大學的科研戰略佈局中重要一環。2019年澳門大學科技學院成立區域海洋研究中心,深入開展海洋領域相關前沿課題研究、助力澳門社會與粵港澳大灣區的可持續發展。相信這次與蘇伊士及澳門自來水股份有限公司的戰略合作將會成為澳門產學研合作的典範。
蘇伊士亞洲地區水務首席執行官方恒業表示,這次是企業與高校的一次戰略性強強合作,意義重大,是我們在保護海洋上的強烈願望和一致理念的體現。蘇伊士集團自19世紀末以來已致力於保護和修復自然環境要素:水、土壤和空氣。集團在全球發動的‘SUEZ4Ocean’,更使其來自五大洲的9萬名員工身體力行參與其中,用實際行動守護海洋。此外,作為終結塑料垃圾全球聯盟(AEPW)的創始成員,蘇伊士聯合40多家國際企業,致力消滅環境中尤其是海洋中的塑料污染物。我深信,今天與澳門大學達成的合作,將進一步發揮澳門大學和蘇伊士在海洋環境與工程研究領域的特長優勢,以及澳門自來水35年來在中國水行業優質服務和智慧化管理方面的標杆經驗,以產學研模式的深度融合,服務澳門大灣區的高質量發展和全球海洋生態的可持續發展。
澳門大學
澳門大學成立於1981年,是粵港澳大灣區西岸地區最優秀,也是澳門特區唯一一所國際化綜合性公立大學。澳門大學在2020年泰晤士高等教育世界大學排名301-350 、亞洲大學排名37、國際化發展第九、全球年輕大學排名52。澳門大學科技學院於2019年成立區域海洋研究中心,深入開展海洋環境、海洋工程和海洋災害等領域的學術前沿課題,推進區域海洋相關課題的學術交流與合作,助力澳門社會乃至粵港澳大灣區的長遠發展。
蘇伊士
蘇伊士集團自19世紀末以來,不斷積累專業知識,通過保護人類健康並支持經濟增長,助力人們持續提高生活質量。蘇伊士及旗下90,000萬名員工遍布全球五大洲,致力於保護和修復我們的自然環境要素:水、土壤和空氣。在水務管理、固廢回收再造、土壤修復和空氣治理等方面,蘇伊士提供富有彈性的創新型解決方案,通過“智慧”城市優化市政和各行業的資源管理,提升其環境和經濟效益。集團向6,400萬人提供環境服務,生產飲用水71億立方米。蘇伊士還為經濟發展做出了積極貢獻,每年直接或間接創造了20多萬個就業崗位,作為新資源的提供者,生產了420萬噸再生原料。集團的目標是在2030年前提供100%的可持續解決方案,為我們的環境、健康和氣候帶來積極影響。蘇伊士集團2019年的總收入達180億歐元。
蘇伊士在亞洲
蘇伊士在早於60年前就進入東南亞,繼而擴展至大中華區的發展也逾40年。蘇伊士現已成為各大城市和工商客戶的首選合作夥伴,提供的水務和固廢管理解決方案,能助其優化資源管理,提升其環境和經濟效益並符合監管標準。集團旗下逾9,000名員工遍布亞洲各地,合作項目逾70個,至今已建造了460多座水處理廠和污水處理廠並向逾3,200萬人口提供水務和固廢資源管理服務。蘇伊士被公認為最具影響力的企業之一,也是環境服務行業的標杆企業。目前蘇伊士在澳門運營著中國水務行業的第一個PPP項目,在上海運營著亞洲其中一座最大的危廢處置設施,同時在泰國也運營著塑料回收再造項目。作為香港固廢處理行業的領導者,蘇伊士集團還為亞洲20個工園區提供專業的環境管理服務。
澳門自來水股份有限公司
澳門自來水股份有限公司於1935年創立,由法國蘇伊士集團和香港新創建集團有限公司組成的蘇伊士新創建有限公司於1985年購入85%股份入主澳門自來水成為主要股東,並與當時澳葡政府簽訂一項為期25年的供水專營合約。合約於2009年獲澳門特別行政區政府延長20年至2030年7月。公司以專業技術及優質服務,為澳門提供可靠安全的供水服務,保證水質符合及優於歐洲飲用水衛生標準。公司的願景是與客戶建立親切緊密的關係,為客戶、股東、員工及社會各界友好創造價值,為澳門的繁榮與發展作出貢獻。

澳大與蘇伊士開展創新研究保護海洋
科研佈局新進展 澳大區域海洋研究中心揭牌
澳門大學科技學院的“區域海洋研究中心”舉行揭牌儀式,標誌著澳大全面推進在區域海洋領域的研究,助力澳門經濟多元發展,為粵港澳大灣區的長遠發展做出貢獻。
儀式上,澳大校長宋永華、副校長葛偉、科技學院院長須成忠和區域海洋研究中心代主任周萬歡主持揭牌。宋永華致辭時表示,面對澳門特區政府於海洋利用、海洋防災減災與海洋環境保護的挑戰,澳大特意在科研戰略佈局中重點建設區域海洋新興研究領域。區域海洋研究中心的成立標誌著大學將深入展開與海洋領域相關的前沿課題研究。此舉將促進澳門與其他國家在海洋領域的交流與合作,同時幫助澳門實現經濟多元化發展,為粵港澳大灣區的長遠發展做出貢獻。
澳大區域海洋研究中心聚焦海洋多圈層動力與環境調節機制、濱海城市自然災害與工程、濱海環境治理與資源開發三個方向。周萬歡致辭時提到鑒於澳門近年先後經歷兩次風災,首要工作是解決目前海洋環境與工程方面等的科學問題,以提升澳門在海洋防災減災、海洋工程建設與維養、海洋生態環境保護、海洋資源利用等方面的水平。目前中心在相關研究領域有超過十個實驗室及多個在建實驗室,包括“海洋環境污染檢測實驗室”、“海洋環境污染防治與修復實驗室”、“海域環境污染模擬實驗室”、“環境生物技術實驗室”、“水利工程實驗室”等。
澳大區域海洋研究中心將積極貫徹落實澳大制定的“三個三”科研戰略佈局,積極拓展科技建創新平台,形成創新引領發展的新局面。“三個三”是指以三間國家重點實驗室、三個重點發展方向、三個跨學科交叉領域為骨幹的科研戰略佈局。目前,該中心已與青島海洋科學與技術試點國家實驗室、中國科學院海洋研究所、中國科學院南海海洋研究所、海洋污染國家重點實驗室、海岸和近海工程國家重點實驗室、污染控制與資源化研究國家重點實驗室等國家及大灣區頂級的海洋相關領域科研單位開展了密切合作。未來將著眼於澳門海洋科學發展所需,為澳門培養更多海洋領域專業人才,提升澳門在海洋科學領域的國際地位與影響力,為大灣區乃至國家的海洋科技發展做出貢獻。
參與儀式的嘉賓還包括:澳大研究服務及知識轉移辦公室主任楊志新教授,澳大區域海洋研究中心成員林智超教授、顏王吉教授、陸萬海教授、黎永杰教授、郝天偉教授、張平教授、施華斌教授、申平教授、高亮教授和蔡忠亞教授。





大型土木工程結構參數識別的振動傳遞比方法及其應用研究

在研究工程結構動力災變機理、健康監測和安全評估時,一個首先需要解決的關鍵問題就是正確地識別或監測結構的動力特性或參數,這些參數是研究結構災變機理、健康監測和安全評估的基礎和依據。參數識別屬於系統識別範疇,一般意義上講,就是在觀察到的系統輸入(激勵)和輸出(回應)資料的基礎上,對系統確定一個數學模型,要求這個模型盡可能精確地反映系統的特性,從而達到識別系統參數的目的。系統識別原本是現代控制理論研究的基本問題之一,近年以來已愈來愈在各類工程結構中顯示出潛在的應用前景,是學科滲透和結構工程專業概念拓寬的一個典型實例。

結構動力特性研究結構災變機理、健康監測和安全評估的基礎和依據
目前常用的結構參數識別方法通常可以分為兩類。一類是建立在系統輸入和輸出資料基礎上的識別方法。在工程結構振動試驗中, 這類方法需要測量結構的激勵(輸入)和動力回應(輸出),求出反應輸入-輸出關係和系統固有特性的傳遞函數,然後建立傳遞函數與系統參數之間的關係,從而識別出結構的特徵參數。另一類是僅建立在輸出資料基礎上的系統識別方法。這類方法直接利用車輛、行人、風荷載等作用於結構上的日常環境激勵作為系統的輸入,僅根據結構的回應資料完成參數的識別過程。為了便於數學處理,僅基於輸出資料的參數識別方法通常對輸入模型做了理想化假定。然而,這些理想化條件在實際工程中很難得到嚴格滿足,在陣風、車輛等環境荷載激勵下,很多時候工程結構難以避免地受到複雜激勵的作用,如有色雜訊激勵甚至是諧波激勵,實踐與理論的差異無疑會影響系統識別結果的魯棒性與準確性,甚至會導致識別出錯誤的結果。因此,有必要在系統識別階段引入新的方法來充分考慮輸入的影響,為土木工程結構動力災變和安全監測分析提供更穩健可靠的基礎和依據。
 |
 |
工程結構監測資料表明振動傳遞比具有獨特的物理特性和統計規律
 |
 |
振動傳遞比之特性可以用於快速地識別複雜環境激勵下的結構動力特性
近年來,振動傳遞比函數因為其諸多優點成為了系統識別領域重要的分析手段。與頻響函數反映動力系統輸入-輸出的關係不同,振動回應傳遞比函數反映的是系統輸出-輸出之間的關係。因此,應用振動回應傳遞比函數時,系統輸入只作為動力源而不需要參與運算,因此避免了對系統荷載測量的依賴,從而有效地避免了輸入資料的測量。同時,振動回應傳遞比函數可以有效地避免對系統輸入的白色雜訊假定。通過近十餘年時間的探索,課題組在振動傳遞比的固有特性分析和參數識別方法方面取得了一系列富有創新特色的研究成果:(i)提出了功率譜傳遞比(簡稱PSDT)新概念,證明瞭複數域比例函數極限定理,揭示了PSDT在系統極點處獨立於參考輸出和激勵的位置且與兩測點的振型比值等價的物理特性;(ii)基於PSDT的物理特性,建立了PSDT驅動的結構參數識別峰值法和最小二乘複頻域方法,建立了穩定圖剔除虛假模態; (iii)證明瞭複數域比例隨機向量統計推斷定理,揭示了振動傳遞比的統計規律,建立了解析概率模型實現振動傳遞比測量不確定性表徵;(iv)基於振動傳遞比解析概率模型,提出了貝葉斯傳遞比方法實現特徵參數識別不確定性快速量化;(v)推導出了特徵參數變異係數關於不同隨機源的近似閉合解,闡明瞭不同特徵參數之間的相關程度,揭示了特徵參數不確定性的傳播機理。相關成果在國內外著名期刊發表論文12篇;曾獲省自然科學二等獎、省自然科學優秀學術論文一等獎、教育部提名國家自然科學二等獎;被澳大利亞工程院院士Hong Hao教授和上海交大國家傑青、長江彭志科教授等在內的學術同行發表的25篇論文直接跟蹤拓展,10餘篇論文在標題中直接採用了首創名詞PSDT;振動傳遞比理論在10餘座土木工程結構中得到成功應用。
相關文章
- Wang-Ji Yan and Wei-Xin Ren (2012): Operational modal parameter identification from power spectrum density transmissibility. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, Vol.27, No.3, pp.202-217.
- Wang-Ji Yan and Wei-Xin Ren (2013): Use of continuous wavelet transmissibility for operational modal identification. Journal of Structural Engineering, ASCE, Vol.139, No.9, pp.1444-1456.
- Wang-Ji Yan and Wei-Xin Ren (2015): An enhanced power spectral density transmissibility (EPSDT) approach for operational modal analysis: theoretical and experimental investigation. Engineering Structures, Vol. 102, pp.108-119.
- Wang-Ji Yan and Wei-Xin Ren (2016): Circularly-symmetric complex normal ratio distribution for scalar transmissibility functions. Part I: Fundamentals. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 80, pp.58-77.
- Wang-Ji Yan and Wei-Xin Ren (2016): Circularly-symmetric complex normal ratio distribution for scalar transmissibility functions. Part II: Probabilistic models and validation. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 80, pp.78-98.
- Wang-Ji Yan and Wei-Xin Ren (2018): Circularly-symmetric complex normal ratio distribution for scalar transmissibility functions. Part III: Application to statistical modal analysis. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 98, pp. 1000-1019.
- Wang-Ji Yan, Meng-Yun Zhao, Qian Sun and Wei-Xin Ren (2019): Transmissibility-based system identification for structural health monitoring: Fundamentals, approaches and applications. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 117, pp. 453-482.
- Wang-Ji Yan and Lambros Katafygiotis (2019): An analytical investigation into the propagation properties of uncertainty in a two-stage fast Bayesian spectral density approach for ambient modal analysis. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 118, pp. 503-533.
大氣環境中的空氣質量預測和模擬
透過對大氣環境中的空氣質量進行預測和模擬,了解澳門空氣質量每日變化的規律,影響因素與機制。


To strive for the continuous improvement of the urban air quality in Macau, our researches focus on two aspects, i.e., the ambient air quality forecasting and modelling. Following examples are some recent research outcomes:
Development of a statistical forecasting model for PM2.5 in Macau based on clustering of backward air mass trajectories
Macau is a small coastal city (~30.8 km2) in the southwestern side of the Greater Bay Area. Due to its small geographical area, statistical modelling techniques are more computationally efficient and require less input information for fulfilling the purpose of operational air quality forecasting. During the model development, it is convenient to reflect the influence of local emissions and dispersion on the air quality within the city. However, it is difficult to include the effects of transboundary pollution since there is limited information addressing the transporting pathways to Macau from various source regions. Simply speaking, the source of transboundary pollution to Macau is not known. Therefore, this study attempted to address this issue in the daily forecasting model of PM2.5 in Macau by using the clustered backward air mass trajectories of HYSPLIT from 2015 to 2017. The cluster based forecasting model was found to be more efficient (~11% improvement in the critical success index) in capturing the pollution episodes compared to the ordinary model.


Cluster based forecasting model of PM2.5 was found to be more efficient in capturing the pollution episodes compared to the ordinary model
Predicting ground-level ozone concentrations by adaptive Bayesian model averaging of statistical seasonal models
Apart from PM2.5, the ground-level ozone is another major air pollutant of Macau or other cities in the Greater Bay Area. It is a secondary pollutant formed by the photochemical reaction of the ozone precursors (NOx, VOC). The daily variation of this pollutant has strong seasonal cycle throughout the entire year, meaning that it may not be completely described by a single model. Therefore, this study addressed the problem by proposing three ozone prediction models in different periods of the year (ozone season, non-ozone season, and the transitional period). However, sudden switching of models to their designated period in annual forecasting system may affect their performance, especially starting and ending dates of the transitional period can vary yearly. Therefore, the present study also addressed the second problem by using the adaptive Bayesian model averaging scheme. This scheme continuously evaluates the probabilities of all ozone prediction models based on the most recent ozone level. Then, the predicted ozone concentration by this scheme is obtained from the weighed sum of the model outputs according to their probabilities. Based on the measured ozone concentrations at the Taipa ambient station of the Macau Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau, results were proved to be satisfactory.


Adaptive Bayesian Model Averaging Scheme to perform averaging of ozone predictions from several models for DMA8 based on the conditional probability of each model throughout the year.
Bias correction of deterministic air quality model WRF-EURAD
The deterministic air quality model, which is the combination of the meteorological model and the chemical transport model, is widely accepted as the tool to perform operational air quality forecasting due to the large spatial coverage and its ability to explain the mechanism of the predicted pollution episodes (e.g. land-sea breeze, cold front, tropical cyclone, etc.). However, the accuracy of prediction relies on precise input information such as land cover, emission inventories, initial & boundary conditions from the global scale model, etc. Therefore, the accumulation of these uncertainties usually leads to the forecast bias. Empirical correction of the model output based on the measured pollutant concentration at the monitoring station (a.k.a. bias correction) is commonly used for improving the forecast performance. The present study attempted to develop an adaptive bias correction model by using a two-stage approach. First, a systematic selection of the most plausible bias correction model among the candidates was carried out by using the Bayesian model selection approach. Then, the Kalman filter was further implemented onto the selected model in order to transform it into an adaptive bias correction model. The two-stage approach was applied to the case study which corrects the model output of WRF-EURAD for one-day ahead prediction of PM10 concentration in Porto, Portugal. Based on the training data, the selected model at each station was found to have significantly higher probability than the other candidates, and it is also much simpler than the full model. As for the evaluation period, the corrected forecasts by the adaptive bias correction model show significant improvement over the raw outputs of WRF-EURAD. The results confirmed the success of the proposed technique.



Implementation of the Kalman filter on the selected bias correction model can significantly reduce the forecast bias of PM10 concentrations in Porto, Portugal
ALL-IN-ONE Air quality modelling system applied to Macau
Air quality is one of the main environmental concerns by the Macau citizens in recent years. This region is highly affected by the pollution of respirable particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5). The sources of PM comprise of the local anthropogenic sources (road, maritime and air transport as well as domestic, industries and construction activities) and the external influence of air pollution from its neighboring regions. Notwithstanding the potential use of air quality modelling to provide scientific advice on atmospheric emission reduction strategies, air quality forecast, air pollution assessment and air quality regulations at several spatial scales, there are only few air quality modelling applications over the Macau SAR. This study designed a multi-scale air pollution modelling system (ALL-IN-ONE) to provide scientific advice to the policy makers in their strategic planning to improve the air quality and to assess the PM pollution phenomena over Macau. The ALL-IN-ONE is based on the selection of a set of models able to reproduce the meteorological and air quality patterns, from regional to local scales. The system revealed a good performance for meteorological and air quality modelling simulations. From the modelling results, it was found that Macau was affected by air pollution transport from the neighboring regions and population was exposed to the high PM levels over entire study area. Although the tested reduction scenarios of local sources showed a reduction of PM level, several exceedances of daily concentrations were still observed. Therefore, it is necessary to join efforts with neighboring regions to discuss/apply air pollution reduction measures in order to improve the air quality of Macau. The results of this work demonstrated the importance of integrated use of modelling tools to study air pollution phenomena over Macau (ranging from regional to local scales) to define efficient air quality management strategies.

ALL-IN-ONE is an integrated modelling system addressing the contribution of air pollution of Macau from regional scale, urban scale to local scale
相關文章
- Li, X., Lopes, D., Mok, K.M., Miranda, A.I., Yuen, K.V. and Hoi K.I. (2019) Development of a road traffic emission inventory with high spatial-temporal resolution in the world’s most densely populated region-Macau, Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, Vol. 191(4), 239 | DOI: 10.1007/s10661-019-7364-9
- Lopes, D., Ferreira, J., Hoi, K.I., Miranda, A.I., Yuen, K.V. and Mok K.M. (2019) Weather Research and Forecasting Model Simulations over the Pearl River Delta Region, Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, Vol. 12(1), 115-125.
- Liu, B., He, M.M., Wu, C., Li, J., Li, Y., Lau, N.T., Yu, J.Z., Lau, A.K.H., Fung, J.C.H., Hoi, K.I., Mok, K.M., Chan, C.K., Li, Y.J. (2019) Potential Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Black Carbon on Jogging Trails in Macau, Atmospheric Environment, Vol. 198, 23-33.
- Mok, K.M., Yuen, K.V., Hoi, K.I., Chao, K.M. and Lopes, D. (2018) Predicting Ground-level Ozone Concentrations by Adaptive Bayesian Model Averaging of Statistical Seasonal Models, Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, Vol. 32(5), 1283–1297.
- Hoi K. I., Mok, K. M., Miranda, A.I., Yuen, K. V., Monteiro, A., Ribeiro, I., and Lopes, D. (2018). 利用簡約函數形式對數值空氣品質預報系統進行自我調整偏差修正, 兩岸四地環境科技創新與合作青年學者論壇, August 4, Hefei, China.
- Lopes, D., Ferreira, J., Yuen, K.V., Borrego, C., Hoi, K.I., Miranda, A.I. and Mok, K.M. (2018) Desenvolvimento de um Sistema Multi-Escala de Modelação da Qualidade do ar sobre a Região Administrativa Especial de Macau, CIALP – 1º Conferência Internacional de Ambiente em Língua Portuguesa, 8-10 May, Aveiro, Portugal.
- Liu, B., He, M.M., Hoi, K.I., Mok, K.M. and Li, Y.J. (2017) Potential Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Black Carbon on Jogging Trails in Macau, Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Regional Air Quality Management in Rapidly Developing Economic Regions, 16-19 November, Guangzhou, China.
- Mok, K.M., Miranda, A.I., Yuen, K.V., Hoi, K.I., Monteiro, A. and Ribeiro, I. (2017) Selection of Bias Correction Models for Improving the Daily PM10 Forecasts of WRF-EURAD in Porto, Portugal, Atmospheric Pollution Research, Vol. 8(4), 628-639.
- Hoi, K.I., Chio, C.W., Lopes D., and Mok, K.M. (2017) Seasonal Difference of PM10 Exposure in a Diesel Bus, The 5th International Symposium on Regional Air Quality Management in Rapidly Developing Economic Regions, 16-19 November, Guangzhou, China.
- Lopes, D., Hoi, K.I., Mok, K. M., Miranda, A.I., Yuen, K. V. and Borrego, C. (2016) Air Quality in the Main Cities of the Pearl River Delta Region, Global NEST Journal, Vol. 18, no.4, 794 – 802.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V., Mok, K. M., Miranda, A.I. and Ribeiro, I. (2016), Comparison of the Offline and the Online Bias Correction of the WRF-EURAD in Porto, Portugal. In: S. Sauvage, J.M. Sánchez-Pérez & A.E. Rizzoli, (Eds.), Proceedings of the 8th International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software, July 10-14, Toulouse, France, Vol. 2, 377 – 383.
- Lopes, D., Ferreira, J. Hoi, K. I., Mok, K. M., Miranda, A. I. and Yuen, K. V. (2016), WRF-CAMx Application to the Pearl River Delta Region, Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes (HARMO 17), May 9-12, Budapest, Hungary, 121-125.
- Lopes D., Hoi K.I., Mok K.M., Miranda A.I., Yuen K.V., Borrego C. (2015). State of the Air Quality in the Main Regions of Pearl River Delta. Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, September 3-5, Rhodes, Greece, 5pp.
- Mok, K. M., Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V., Miranda, A. I., Borrego, C. and Ribeiro, I. (2015) Selection of a Parsimonious Empirical Correction Rule for a Deterministic Air Quality Model, 2015 International Conference on Earth Observations & Societal Impacts and ICLEI Resilience Forum, June 28 – 30, Kaohsiung, Taiwan. (Session Keynote)
- Hoi, K.I., Zhang, D.B., Mok, K.M.and Yuen, K.V. (2014) Association of Human Mortality with Air Pollution of Hong Kong, Toxics, Vol. 2, 158 – 164.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V., Mok, K. M., Miranda, A. I. and Lai, K. U.(2014) Selection of the Daily PM10 Forecasting Model for an Urban Area in the Northern Region of Portugal with the Bayesian Approach, 2014 International Aerosol Conference, Aug. 28 – Sept. 2, Busan, Korea.
- Hoi, K.I., Yuen, K.V. and Mok, K. M. (2013) Improvement of the Multilayer Perceptron for Air Quality Modelling through an Adaptive Learning Scheme, Computers & Geosciences, Vol. 59, 148 – 155.
- Hoi, K. I., Mok, K. M., Yuen, K. V. and Pun, M. H. (2013) Investigation of Fine Particulate Pollution in a Coastal City with a Mobile Monitoring Platform, Global NEST Journal, Vol. 15, no.2, 178 – 187.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2013) Bayesian Model Class Selection of Daily Ground-level Ozone Prediction Model, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Environmental Management, Engineering, Planning and Economics (CEMEPE) and SECOTOX Conference, June 24-28, Mykonos Island, Greece, 425 – 431.
- Chao, K.M., Hoi, K.I., Yuen, K.V. and Mok, K.M. (2012) Adaptive Modelling of the Daily Behavior of the Boundary Layer Ozone in Macau. ISRN Meteorology, Vol. 2012, Article ID 434176, 7 pages. doi:10.5402/2012/434176.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V., and Mok, K. M. (2011) Iterative Probabilistic Approach for Selection of Time-varying Model Classes, Procedia Engineering, 14, 2585 – 2592.
- Hoi, K. I., Mok, K. M., Yuen, K. V. and Pun, M. H. (2011) Assessment of Fine Particulate Pollution in Macau Using a Mobile Monitoring Platform, Proceedings of the 12th International Conference for Environmental Science and Technology, September 8-10, 2011, Rhodes Island, Greece, A, 737-744.
- Hoi, K.I., Yuen, K.V. and Mok, K.M. (2010) Optimizing the Performance of Kalman Filter Based Statistical Time-varying Air Quality Models. Global NEST Journal, Vol. 12, no.1, 27 – 39.
- Hoi, K.I., Mok, K.M., Yuen, K.V., Pun, M.H., Cheng, A.Y.S., Visue, A. and Vong M.H. (2010) Spatial and temporal variation of black carbon pollution in a coastal city accessed using a mobile monitoring platform, Urban Environmental Pollution: Overcoming Obstacles to Sustainability and Quality of Life (UEP2010), 20-23 June 2010, Boston, USA, P1.20.
- Pun, M.H., Hoi, K.I., Mok, K.M., Yuen, K.V., Cheng, A.Y.S., Visue, A. and Vong M.H. (2010) Transforming the WPS measurements from a mobile monitoring platform into PM10 mass concentrations for city air quality assessment, Urban Environmental Pollution: Overcoming Obstacles to Sustainability and Quality of Life (UEP2010), 20-23 June 2010, Boston, USA P1.38.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V., and Mok, K. M. (2010) Is a Complex Neural Network Based Air Quality Prediction Model Better Than a Simple One? A Bayesian Point of View, Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Computational Mechanics in conjunction with the 12th International Conference on the Enhancement and Promotion of Computational Methods in Engineering and Science, Ed. by Lu, J.W.Z., Leung, A.Y.T., Iu, V.P. & Mok, K.M., American Institute of Physics, Melville, NY, Part I, 764 – 769.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2009) Prediction of Daily Averaged PM10 Concentrations by Statistical Time-varying Model, Atmospheric Environment, 43, issue 16, 2579-2581.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2009) Enhancement of Kalman Filter Based Air Quality Predictive System by Using Bayesian Approach, Proceedings of the 11th International Conference for Environmental Science and Technology, September 3-5, 2009, Chania, Crete, Greece, A, 457-466.
- Mok, K. M., Miranda, A. I., Leong, K. U and Borrego, C. (2008) A Gaussian Puff Model with Optimal Interpolation for Air Pollution Modelling, International Journal of Environment and Pollution, Vol. 35, no. 1, 111–137.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2008) Kalman Filter Based Prediction System for Wintertime PM10 Concentrations in Macau, Global NEST Journal, 10, no.2, 140–150.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2008) Time-varying Models for Forecasting Summertime Daily Averaged PM10 Concentrations of Macau, Proceedings of the1st Nanshan District Academic Forum of PhD Candidates’ from Shenzhen, Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan in conjunction with the196th Tsinghua Forum for Doctoral Candidates, November 28-29, 2008,Shenzhen, China, 10pp. (Second Prize of the Best Paper Award)
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2008) An Artificial Neural Network Model for the Prediction of Daily Averaged PM10 Concentrations in Macau, Proceedings of the 6th National Civil Engineering Forum for Graduate Students, November 22-23, 2008, Beijing, China.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2007) Statistical Modeling of PM10 concentrations in Macau by using Kalman filter, Proceedings of the APCOM’07 in conjunction with EPMESC XI (CD-ROM), December 3-6, 2007, Kyoto, Japan, MS41-4-4, 9pp.
- Hoi, K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2007) Applying Kalman Filter to Forecast Short-term Air Quality in Macau, Proceedings of the 10th International Conference for Environmental Science and Technology, September 5-7, 2007, COS Island, Greece, Vol. A, 504-511.
- Chang, S. W., Mok, K. M. and Yuen, K. V. (2007) Association of PM10 Pollution Episodes with the Meterological Conditions in Macau, Proceedings of the 10th International Conference for Environmental Science and Technology, September 5-7, 2007, COS Island, Greece, Vol. B, 90-95.
- Yuen, K. V., Hoi K. I., and Mok, K. M. (2007) On the Selection of Noise Parameters for Kalman Filter, Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, Vol. 6, no. 1, 49 – 56.
- Hoi K. I., Mok K. M., and Yuen K.-V. (2006) Analysis of Wet Acid Deposition in Macau, Global NEST Journal, Vol. 8, no.3, 224 – 233.
- Hoi K. I., Yuen, K. V. and Mok, K. M. (2006) Updating Noise Parameters of Kalman Filter Using Bayesian Approach, Computational Methods in Engineering & Science: Proceedings of the EPMESC X, by Yao, Z.H., Yuan, M.W. & Chen, Y.Q., Tsinghua University Press & Springer, Beijing, 782 – 791. (EPMESC X Student Paper Competition Award)
- Lam, L. H. and Mok, K. M. (2006) Prediction of PM10 Concentrations in Macao with Artificial Neural Network, Computational Methods in Engineering & Science: Proceedings of the EPMESC X, Ed. by Yao, Z.H., Yuan, M.W. & Chen, Y.Q., Tsinghua University Press & Springer, Beijing, 895 – 902.
- Mok, K.M. , Hoi, K.I. and Yuen K.V. (2005) Causes of Wet Acid Deposition in Macau, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, September 1 – 3, 2005, Rhodes island, Greece, Vol. B, 623-628.
- Mok, K. M. and Hoi, K. I. (2005) Effects of Meteorological Conditions on PM10 Concentrations – A Study in Macau, Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, Vol. 102, 201-223.
- Tsai, W. Y., Chan, L. Y., Chan, C. Y., Wong, K. H. and Mok, K. M. (2004) Respirable Suspended Particulate in Macao, The 3rd Asian Aerosol Conference, January 6 – 9, 2004, Hong Kong, (Fri-B2, OAA05).
- Mok, K. M. and Hoi, K. I. (2003) Association of PM10 Concentrations and Wind Directions in Macau, Proceedings of the International Conference on Pollution in Metropolitan and Urban Environment – POLMET 2003 (POLMET CD Rom), Nov. 3-5, 2003, Hong Kong, Session 6A, 6pages.
- Chan, L. Y., Wong, K. H., Chan, C. Y., Tsai, W. Y. and Mok, K. M. (2002) Carbon Monoxide in Urban Roadside Microenvironments of Macao, Proceedings of the Regional Workshop on Better Air Quality in Asian and Pacific Rim Cities (BAQ 2002 CD Rom), Hong Kong, PS-34-1 – PS-34-4.
- Mok, K. M. (2002) Development of an Air-Quality Index Forecasting System for Macau – A Memoir, Investigação Científica Sobre o Ambiente e Desenvolvimento Urbano em Macau, Ed. by Wang, Z.S., Chen, J.N., & Du, P.F., Univ. of Macau, Tsinghua Univ. & National Natural Science Foundation, Macau, 34-46. (Invited Lecture)
- Mok, K. M., Tam, S. C., Hoi, K. I. and Lei, S. I. (2002) Um Sistema “Inteligente” de Previsão da Qualidade do ar em Macau, Revista do Ambiente, ANO 6, No. 20-21, 92-96.
- Mok, K. M., Tam, S. C., Hoi, K. I. and Lei, S. I. (2002) An Intelligent Air-Quality Forecasting System in Macao, Proceedings of the 2001 International Conference and Exhibition on Sustainable Development and Green Enterprises, Ed. By Environment Council, Macao Special Administrative Region, P.R. China, Environment Council, 273-282. (Invited Lecture)
- Mok, K. M., Tam, S. C., Yan, P. and Lam, L. H. (2000) A Neural Network Forecasting System for Daily Air Quality Index in Macau, Air Pollution VIII, Ed. by Longhurst, J.W.S., Brebbia, C.A., & Power, H., WIT Press, Southampton, 41-50.
- Mok, K. M., Tam, S. C. and Wang, Z. S. (1999) Air-Quality Forecasting System in Macau, Proceedings of the 1st Macau Symposium on Environment and City Development, Macau, 78-85.
- Mok, K. M., Tam, S. C., Lam, L. H., and Yan, P. (1999) Prediction of Macau Daily Electricity Consumption with Artificial Neural Network, Computational Methods in Engineering and Science – EPMESC VII, Ed. by Bento, J., Oliveira, E. A. & Pereira, E., Elsevier Science, Kidlington, Oxford, Vol. 2, 827 – 836.
- Tam, S. C., Mok, K. M., Yan, P., and Lam, L. H. (1999) An Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System for the Forecast of Macau Daily Electric Load, Computational Methods in Engineering and Science – EPMESC VII, Ed. by Bento, J., Oliveira, E. A. & Pereira, E., Elsevier Science, Kidlington, Oxford, Vol. 2, 817 – 826.
- Mok, K. M. (1998) INTELAIR-Hybrid System for Urban Air Pollution Management: Artificially Intelligent and Traditional Modelling, Proceedings of S&T Co-Operation with Asia in the Area of Sustainable Management of Natural Resource – A Co-Ordination Meeting in China (CD-ROM), Ed. by J. P. Lobo-Ferreira and Tilak Viegas, CEC-DGXII-INCO-DC and P.R. China-SSTC-DIC. (Invited Presentation)
- Mok, K. M. and Tam, S. C., (1998) Short-Term Prediction of SO2 Concentration in Macau with Artificial Neural Networks, Energy and Buildings, Vol. 28, 279-286.
- Tam, S. C., Mok, K. M. and Sam, C. (1998) Adaptive Fuzzy System for Prediction of SO2 concentration in Macau, Air Pollution VI, Ed. by Brebbia, C.A., Ratto, C.F. & Power, H., WIT Press/Computational Mechanics Publications, Southampton, 277-286.